Performance: Loss, Delay, Throughput
How do loss and delay occur?
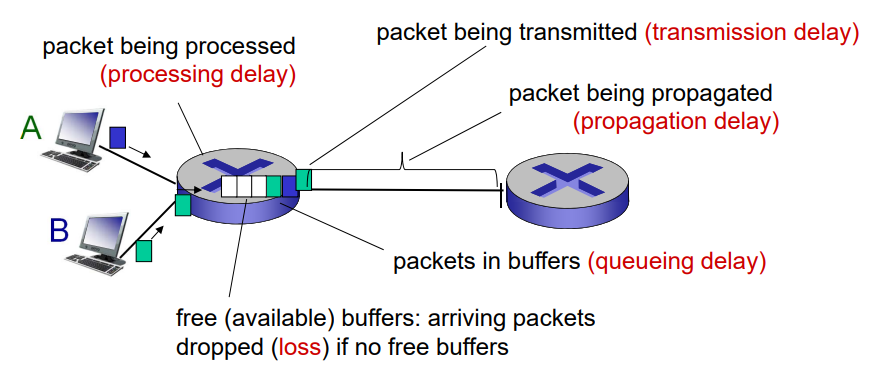
- Packets queue in router buffers --> Packets queue, wait for their turn.
Four sources of packet delay

▶ d-pro: nodal processing
- check bit errors at L2, L3
- determine output link
▶ d-queue: queueing delay
: time waiting at output link for transmission.
- depends on congestion level of router.
▶ d-trans: transmission delay = L/R
- L: packet length (bits)
- R: link bandwidth (bps)
▶ d-prop: propagation delay = d/s
- d: length of physical link
- s: propagation speed
Packet queueing delay (revisited)
▶ Traffic intensity = La/R
- L: packet length (bits)
- a: average packet arrival rate
- R: link bandwidth (bps) - 컴퓨터나 네트워크가 일정 시간 내에 보낼 수 있는 정보량

--> queuing delay는 traffic intensity에 따라 달라진다.
- La/R = 0: queuing delay small
- La/R = 1: queuing delay large
- La/R > 1: queuing delay infinite --> packet loss
Traffic intensity(TI) at Output Queue
- La/R = Average rate at which bits arrive at the queue (bps)/the rate at which bits are pushed out of the queue (bps)
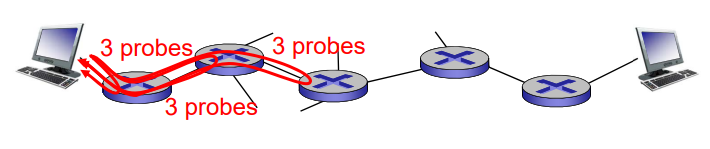
"Real" Internet delays and routes
- traceroute program
: Provides delay measurements from source to router along end-end Internet path towards destination.
Packet loss

- Queue (aka buffer) preceding link in buffer has finate capacity.
--> Packet arriving to full queue dropped (aka lost). - Lost packet may be retransmitted by previous node(loss 복구), by source end system, or not at all.
Throughput
: Rate at which bits are being sent from sender to receiver.
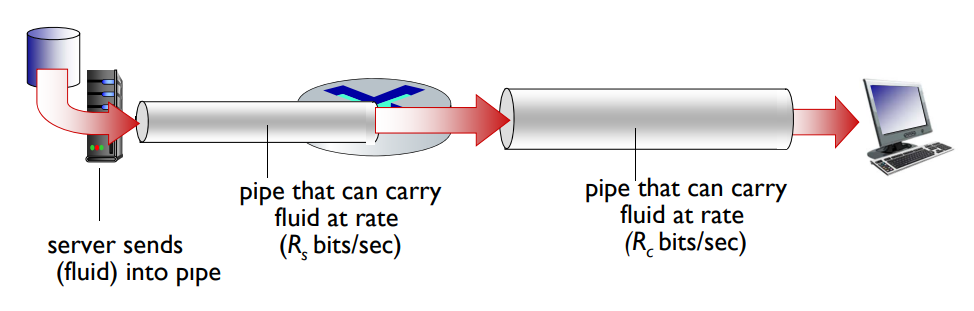
▶ Bottleneck link
: Link on end-end path that constrains end-end throughput.

Throughput: Internet scenario

- Mainly, affected by transmission rate.
- End-end throughput: min(Rc, Rs, R/10)
--> In practice: Rc or Rs is often bottleneck.
--> A link with high transmission rate may be the bottleneck link due to the intervening traffic.
Protocol layers, service models
5-layer Internet protocol stack

▶ Application: supporting network applications.
- FTP, SMTP, HTTP
▶ Transport: process-process data transfer.
- TCP, UDP
▶ Network: routing of datagrams from source to destination.
- IP protocol, Routing protocol
▶ Data link: data transfer between neighboring network elements.
- Ethernet, 802.11 WiFi, PPP
▶ Physical: bits "on the wire".
Encapsulation

▷ Protocol data unit의 이름이 계층별로 다르다.
- Application: message
- Transport: segment
- Network: datagram
- Data link: frame
- Physical
▷ 어떤 계층 앞의 헤더는 앞선 source/switch/router/destionation의 동일 계층에서 보낸 것이다.
'Computer Network > 컴퓨터네트워크' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [컴퓨터네트워크] 2. Application Layer (2) (0) | 2023.09.28 |
|---|---|
| [컴퓨터네트워크] 2. Application Layer (1) (0) | 2023.09.16 |
| [컴퓨터네트워크] 1. Introduction (4) (0) | 2023.09.16 |
| [컴퓨터네트워크] 1. Introduction (2) (0) | 2023.09.07 |
| [컴퓨터네트워크] 1. Introduction (1) (0) | 2023.09.06 |



