2) Distance vector algorithm: Bellman-Ford algorithm
Distance vector (DV) algorithm
: Bellman-Ford (BF) equation 베이스 알고리즘
- Bellman-Ford equation: cost of least-cost path from x to y.
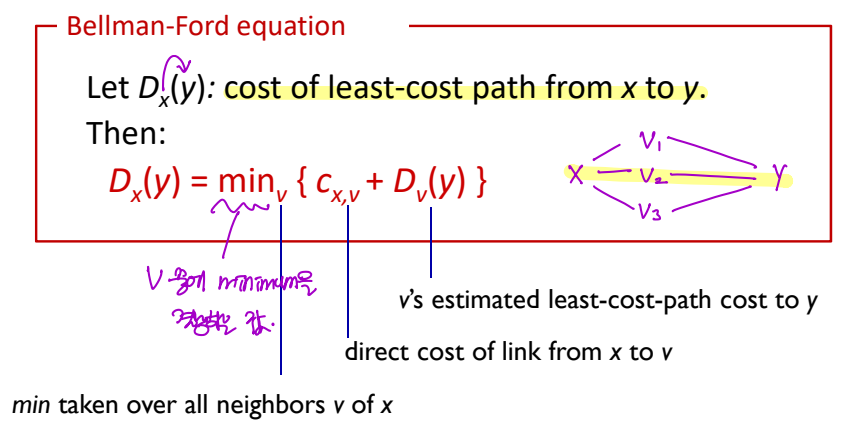
▷ x --> v --> y
: (x~v) + (v~y)의 cost를 가장 낮게 만드는 v를 선택한다.
Bellman-Ford: Example

▷ u --> (v | x | w) --> z
: u --> x --> z의 cost가 가장 낮으므로, 중간 node로 x를 택한다.
- Bellman-Ford 방식: 각각의 이웃(v, x, w)이 목적지(z)로 얼마만에 갈 수 있는지를 알아야 한다. (세상 모든 목적지에 대해!)
Distance vector (DV) algorithm

Source = x, Destination = y, 사이의 node = {a, b, c}라고 할 때,
Dx(y) = x로부터 y까지의 최단거리를 알기 위해서는 {a, b, c} 중 어떤 node를 거쳐야 하는지 알아야 한다.
--> 이웃끼리 자신의 distance vector를 때때로 주고받아서, 결국 모든 목적지에 대해 최단의 distance vector를 계산할 수 있어야 한다.
▶ Distance vector가 변하는 경우:
- x --> {a, b, c}까지의 link cost가 변할 때 (change in local link cost)
- {a, b, c} --> y까지의 link cost 변할 때 (mssage from neighbor)
- 각각의 node는 자기 자신의 link cost가 변했는지, 이웃으로부터 link cost가 변했다는 연락이 오는지 기다린다.
- 만약 distance vector가 변했을 수 있는 둘 중의 하나의 상황이 되면, distance vector를 다시 계산한다.
- 계산한 결과 어떤 목적지로의 distance vector가 변하면, 이웃에게 알린다.
--> 계속 계산하다가, distance vector가 더 이상 변하지 않으면, settle된다.
Distance vector (DV) algorithm: Example



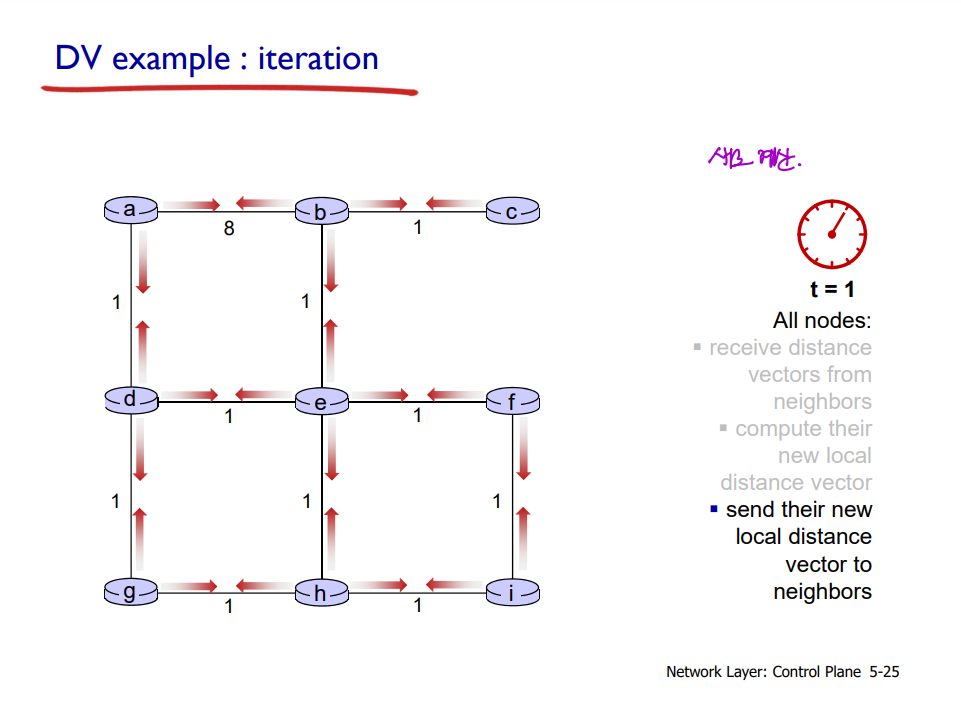


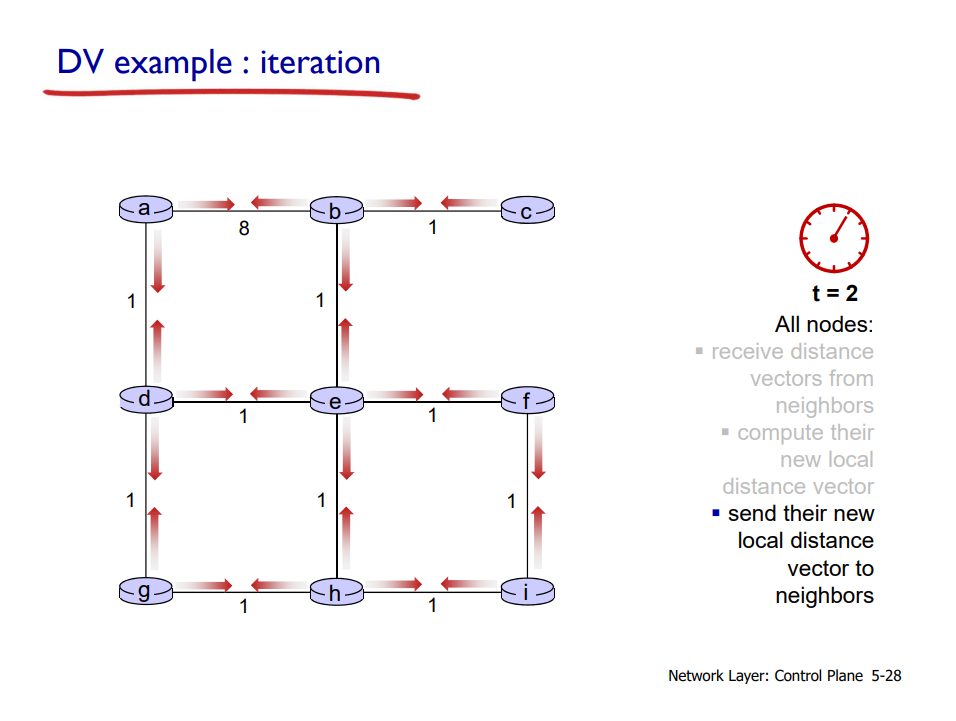
: 나의 distance vector가 더 이상 변하지 않을 때까지 반복한다!


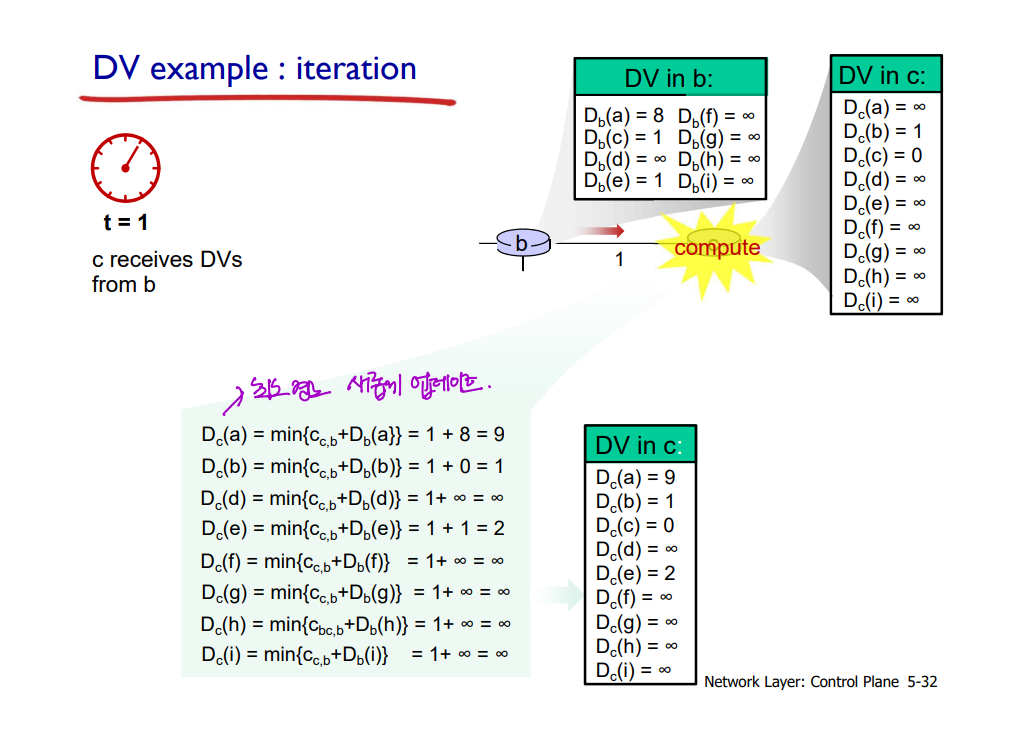
t = 0에서 c의 DV가 어디까지 영향을 미칠까?
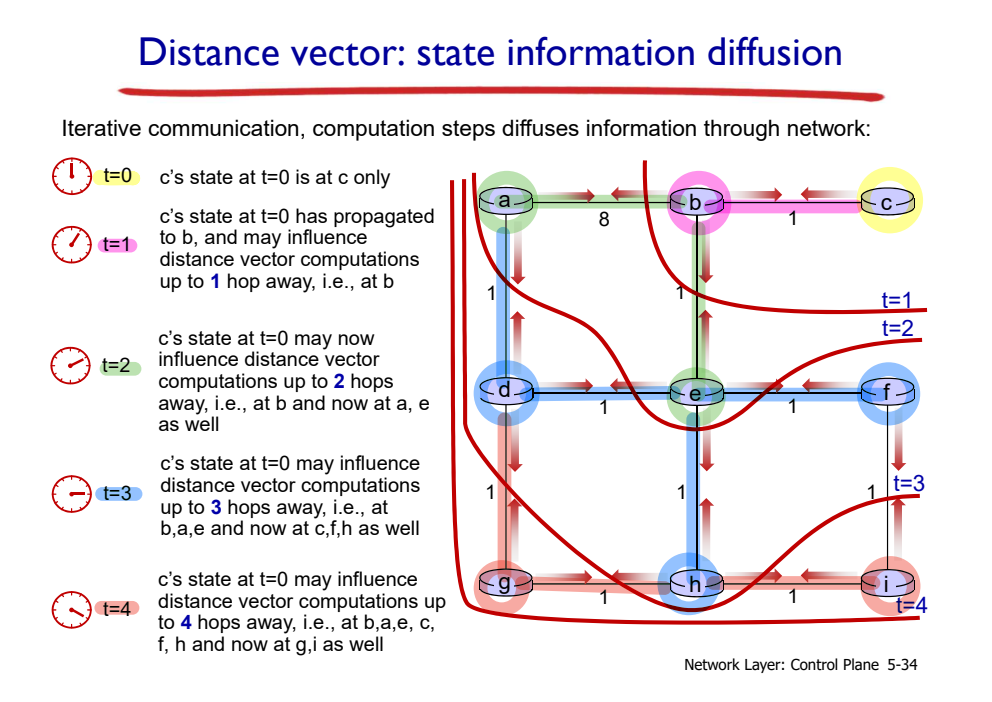
- t=0: 0 hop away
- t=1: 1 hop away
- t=2: 2 hop away
- t=3: 3 hop away
- t=4: 네트워크 전체
--> 네트워크 크기에 따라 점차 퍼져나간다.
Distance vector: link cost changes
▷ "Good news travels fast"
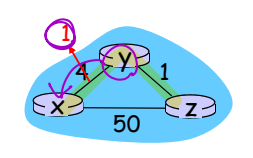
: 인접한 link cost가 줄어들면 distance vector가 변하고, 이러한 변화는 이웃에게 빠르게 전달된다.
- 원래 경로보다 더 좋은 경로가 나타났다! Distance vector를 업데이트한다!
Distance vector's flaw due to link cost changes; count to infinity
▷ "Bad news travels slowly"


▶ Count to infinity: 기존 경로가 나빠졌을 때는 바꿔야 할 경로를 알아차리는 데에 시간이 오래걸린다.
- 원래 경로가 나빠졌다! 어떡해야 돼?...
Count to infinity 문제의 해결책
▶ 2-hop loop에 대해서는:

- Split horizon: A --> B --> C인 상황에서는, A가 C까지의 경로를 B에게는 알리지 않는다. (혼란을 막음)
- Split horizon with poisoned reverse: A --> B --> C인 상황에서, A가 C까지의 경로를 B에게 알리기는 하지만, '무한대'라고 알린다.
--> But, it does not work for routing loops involving 3 or more nodes...

LS(Link-state routing algorithm) vs. DV(Distance vector algorithm)

▶ Router가 cost 정보를 알려주는 대상, 알려주는 cost 정보:
- LS: 세상의 모든 router에게, 자신과 붙어있는 router와의 direct link cost를 broadcast한다. (Dijkstra's algorithm)
- DV: 자신과 인접한 router에게만, 세상 모든 목적지에 대해 내가 알고 있는 경로 길이를 알려준다. (Bellman-Ford algorithm)
▶ Message complexity:
- LS: O(n*E) --> More, smaller messages (더 많은 router들에게, 작은 메시지를 보낸다.)
- DV: O(n-1) --> Fewer, larger messages (자신과 인접한 router들에게만, 큰 메시지를 보낸다.)
▶ Speed of convergence:
- LS: O(n^2)
- DV: count-to-infinity problem때문에, convergence time이 경우에 따라 다르다.
▶ Robustness: What happens if router malfunctions or is compromised?
- LS: 좁은 부분에 대해서는 망가지지만, 다른 부분은 괜찮다.
- DV: Error propagates through network! (네트워크 전체에 문제가 퍼져나간다!)
Hierarchical routing
Making routing scalable
Routing protocol이 엄청 다양하네?
이러한 routing algorithm에는 문제가 많다...
- 확장성 문제
- Administrative autonomy (행정 자치) 문제: 독자성을 보장받고 싶다! --> Autonomous Systems (AS)
Hierarchical routing: Autonomous Systems (AS)

▷ 하나의 AS 안에서는:
- 동일한 routing policy를 적용한다.
- Single ownsership 하에 있다.
- Unique 32-bit integer AS number (ASN)에 의해 식별된다.
Internet approach to scalable routing
실질적으로는 각 AS에 마다 자신만의 고유한 routing protocol을 갖는다.
▶ Routing protocol 종류 2가지:

- Intra-AS routing: 하나의 AS 내에서의 routing (예: OSPF, RIP)
- Inter-AS routing: AS 간의 routing (예: BGP)
- 하나의 AS는 gateway를 통해 다른 AS와 연결된다.
: AS --> gateway routers --> AS
Interconnected ASes
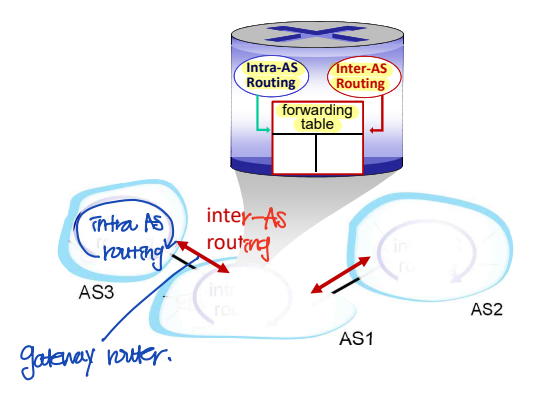
- Intra-AS routing: 하나의 AS 내에서 destination을 결정한다. (Intra-AS routing protocol --> Forwarding table)
- Inter-AS routing: External destination을 결정한다.
▶ Gateway router: 서로 다른 AS들을 연결하는 router (각각의 AS 연결마다 다름)
--> Forwarding table: Intra-AS routing과 Inter-AS routing의 결과가 합쳐져서 만들어진다.

출처: 이화여자대학교 이미정교수님 컴퓨터네트워크
'Computer Network > 컴퓨터네트워크' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [컴퓨터네트워크] 1129 (1) | 2023.12.02 |
|---|---|
| [컴퓨터네트워크] 1124 (1) | 2023.11.27 |
| [컴퓨터네트워크] 1117 - Ch5. Network Layer: Control Plane (1) | 2023.11.17 |
| [컴퓨터네트워크] 1115 (0) | 2023.11.15 |
| [컴퓨터네트워크] 1110 (0) | 2023.11.11 |



