- SDN (Software Defined Networking)
지금까지 traditional routing에 대해 배웠다. 이제 SDN에 대해 알아보자.
Traditional Internet: Per-router Control Plane
- Traditional routing의 problem: "monolitic" router (하드웨어부터 어플리케이션까지 하나로 묶여 있다.)
- Solution: "middlebox"
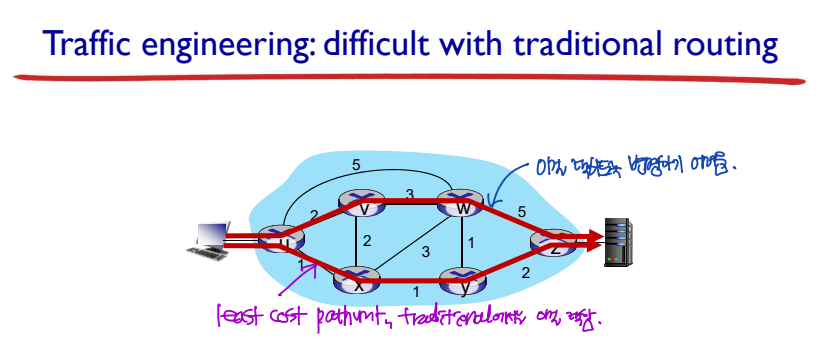
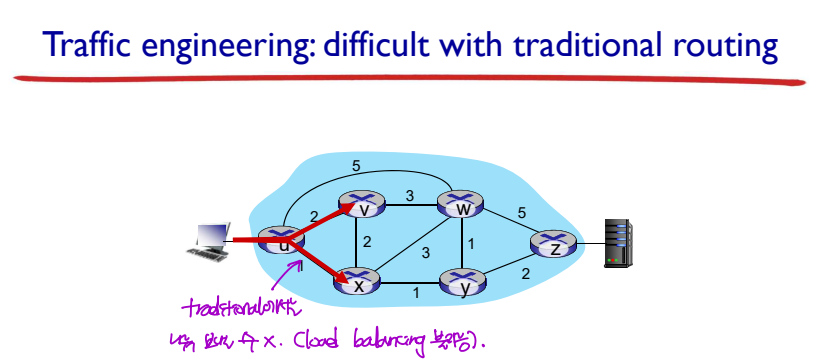
Traffic Engineering: Difficult with Traditional Routing
- Traffic engineering: traffic이 거쳐가는 길을 조정하는 것
--> Traditional routing에서는 traffic engineering이 어렵다.

--> SDN: Generalized forwarding
SDN: How?
: Data plane과 Control plane을 분리한다.
- Control plane: Logically centralized control plane (server)를 둔다.
- Data plane: "match & action"
▷ Logically centralized control plane!
- Easier network management.
- Programmable router: centralized programming.
- Open (non-proprietary) implementation of control plane.\
SDN control plane
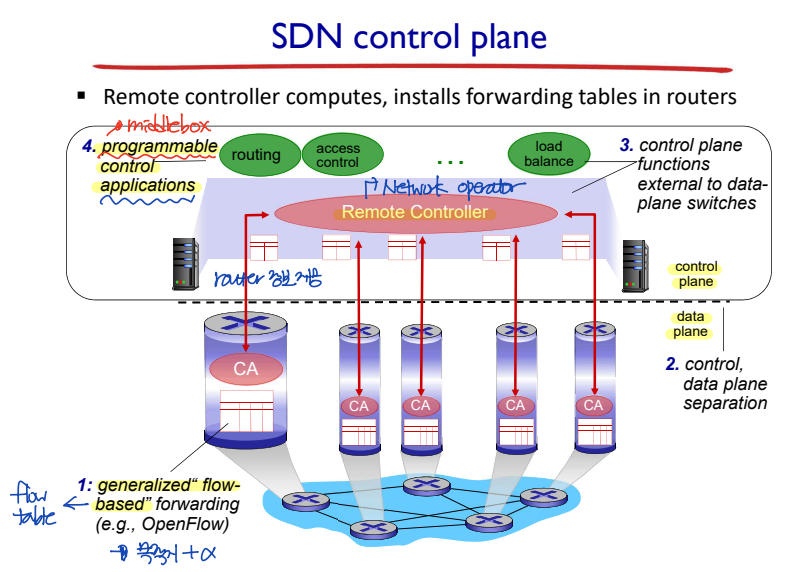
- Generalized, flow-based forwarding: flow table <--> 목적지 기반 forwarding, forwarding table
- Control plane과 Data plane이 분리되어 있다.
- Control plane: Remote controller + Programmable control applications
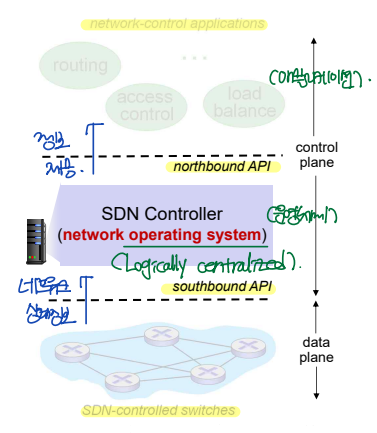
SDN logical structure
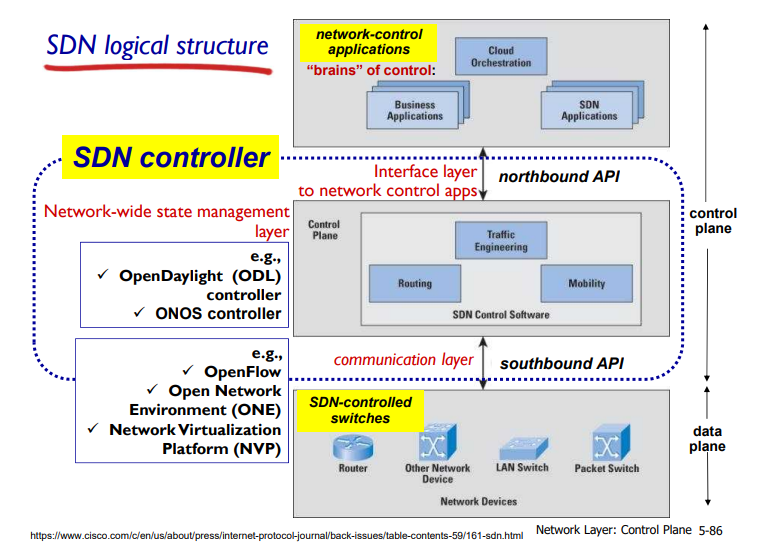
▶ Control plane:
- network-control applications
- northbound API
- SDN controller
- southbound API
▶ Data plane
- SDN-controlled switches
1) Data plane: switches

: Generalized forwarding 역할만을 하드웨어적으로 수행한다.
- SDN controller로부터 flow table을 받아오는데, 이때, southbound API를 통해 소통한다. southbound API의 대표적 예시로 OpenFlow protocol이 있다.
2) Control plane: SDN controller
- southbound API를 통해, SDN-controlled switch로부터 네트워크 상태 정보를 받아온다.
- 네트워크 상태정보를 유지한다.
- northbound API를 통해 network-control application에게 네트워크 상태정보를 제공한다.
- SDN controller는 logically centralized 시스템이지만, 실제 구현은 distributed system이다.
- 이유: 성능, 확장성, fault-tolerance, 견고성을 유지하기 위함이다.
3) Control plane: Network-control applications

: Control plane의 "brain" 역할을 한다. --> Implement control functions.
▶ Control plane
- Network-control application: 실제 control function을 구현한다.
- SDN controller: 정보를 유지하고, control function을 switch에게 전달한다.
--> "Unbounded": network-control application, SDN controller, SDN-controlled switches는 서로 다른 제공자에 의해 제공될 수 있다!
Components of "distributed" SDN controller
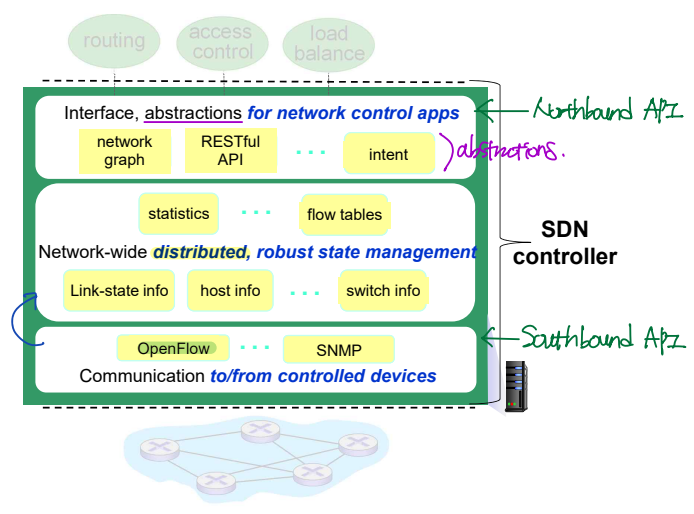
SDN controller에 대해 좀 더 자세히 알아보자.
- Northbound API: SDN controller와 network-control application과의 interface, abstractions.
- SDN controller: network-wide 상태 유지 layer.
- Southbound API: SDN controller와 switch와의 communication layer.
- OpenFlow: 대표적인 southbound API 프로토콜
OpenFlow protocol
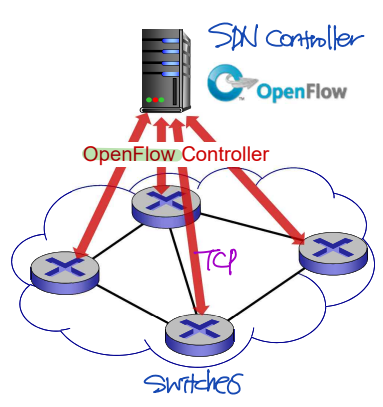
Southbound API의 대표적인 프로토콜인 OpenFlow 프로토콜에 대해 좀 더 자세히 알아보자.
- SDN controller와 switch 사이의 communication layer 역할을 한다.
- 메시지를 전달하기 위해 TCP를 이용한다.
- OpenFlow 메시지에는 세 종류가 있다.
- controller --> switch
- switch --> controller
- controller <-> switch
SDN: contol/data plane interaction - Example
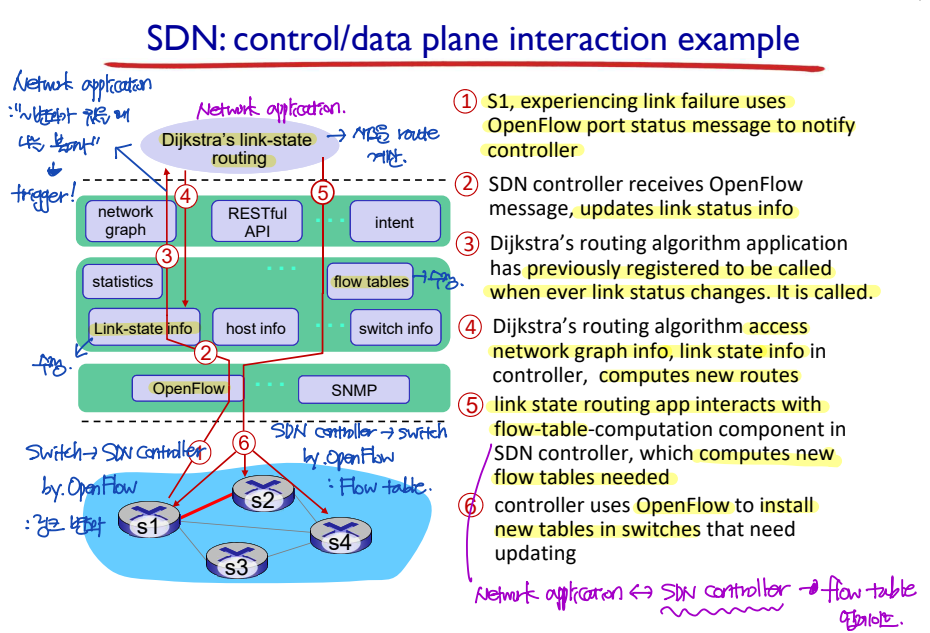
Link state에 변화가 생겼을 때, SDN controller에서 어떻게 새로운 route를 계산하여 새로운 flow table을 만들고, 이를 switch에게 전달하는지 알아보자.
- Switch --> SDN controller: OpenFlow 프로토콜을 이용하여, link state에 변화가 생겼음을 알린다.
- SDN controller: 기존의 link-state information을 수정한다.
- Network-control application은 "~~~ 변화가 있을 때 나를 불러라."라는 메시지를 미리 저장해두었다. 새로운 route 계산이 필요하기 때문에, Dijkstra's link-state routing이라는 network-contorl application을 부른다.
- Dijkstra's link-state routing application: SDN controller의 link state information을 이용하여 새로운 route를 계산한다.
- Dijkstra's link-state routing application: 새롭게 계산된 정보를 통해 SDN controller의 flow table을 수정한다.
- SDN controller --> Switch: OpenFlow 프로토콜을 이용하여, 새롭게 업데이트된 flow table을 switch로 전달한다.
SDN: selected challenges

'Computer Network' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [네트워크] 5.7 네트워크 관리와 SNMP, NETCONF/YANG (0) | 2023.12.10 |
|---|---|
| [네트워크] 5.6 인터넷 제어 메시지 프로토콜(ICMP) (0) | 2023.12.10 |
| [네트워크] 5.4 인터넷 서비스 제공업자(ISP) 간의 라우팅: BGP (1) | 2023.12.10 |
| [네트워크] 5.3 인터넷에서의 AS 내부 라우팅: RIP, OSPF (0) | 2023.12.10 |
| [네트워크] 5.2 라우팅 알고리즘 (0) | 2023.12.10 |



