Instruction
: The words of a computer's language.
- Instruction Set: vocabulary
- Different computers have different instruction sets.
- Early computers had very simple instruction sets.
- Many modern computers also have simple instruction sets.
- We will study RISC-V instruction set in this course.
The RISC-V Instruction Set
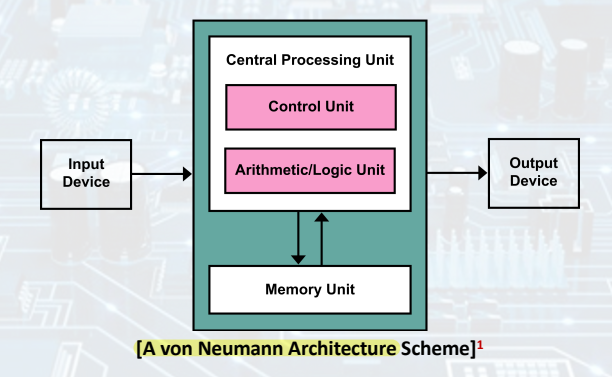
Stored-Program Concept
Arithmetic Operations
: Add and subtract, three operands.
add a, b, c // a = b + c▶ Design Principle 1: Simplicity favors regularity.
Arithmetic Example
f = (g + h) - (i + j);add t0, g, h
add t1, i, j
sub f, t0, t1
RISC-V Assembly Language
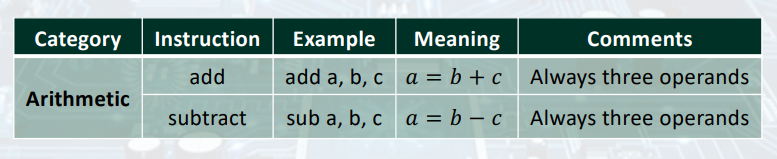
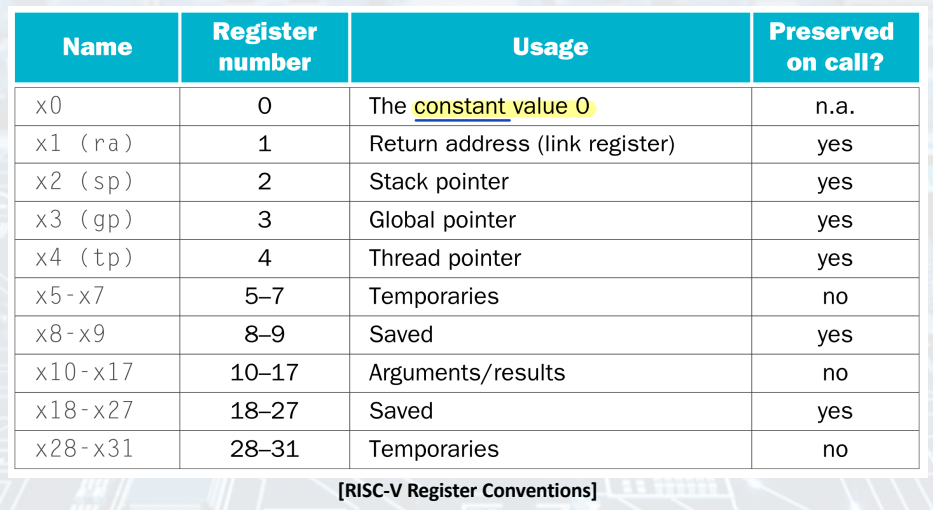
Register Operands
- Arithmetic instructions use register operands.
- RISC-V has a 32 x 32-bit register file.
- word: 32-bit (4-byte)
- 32 x 32-bit general purpose registers x0 to x32.
▶ Design Principle 2: Smaller is faster.
RISC-V Registers
Register Operand Example
f = (g + h) - (i + j);add x5, x20, x21 # x5: temporary variable
add x6, x22, x23
sub x19, x5, x6
Memory Operands
- Main memory is used for composite data.
- To apply arithmetic operations,
- Load values from memory into registers.
- Store result from register to memory. - Memory is byte addressed.
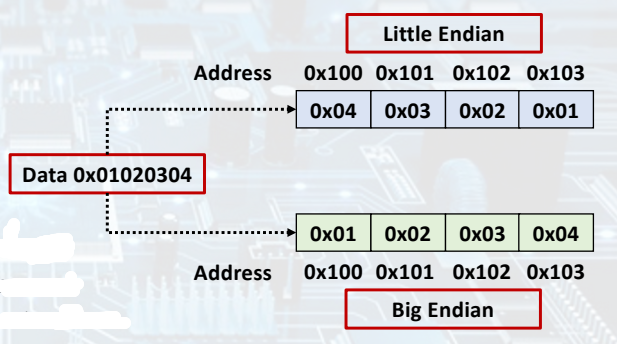
--> Each address identifies an 8-bit. - RISC-V is Little Endian.
- Little Endian: LSB at least address of a word.
- Big Endian: MSB at least address of a word. (MIPS: Big Endian) - RISC-V does not require words to be aligned in memory.
Memory Address
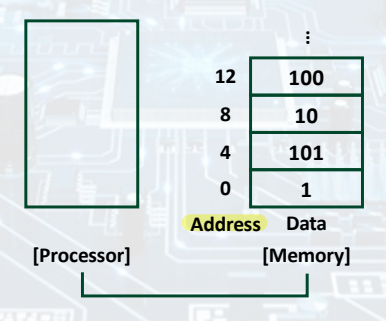
- Word --> 32 bits.
- Byte --> 8 bits.
--> Since 8-bit bytes are useful in many programs, most architectures address individual bytes. (8-bit 즉, 1 byte 단위로 address에 접근한다.)
Load & Store Word
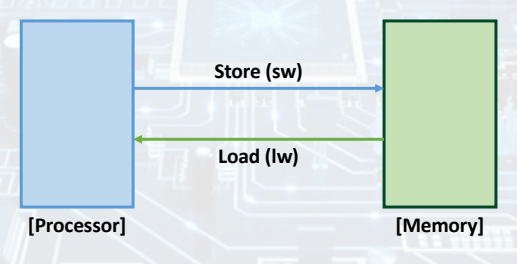
- Load word (lw): The data transfer instructions that copies data from memory to register.
- Store word (sw): The data transfer instructions that copies data from a register to memory.
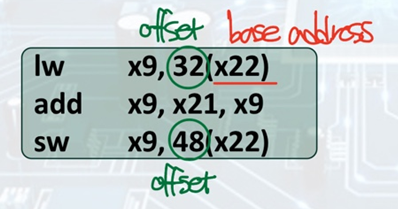
Memory Operand Example
A[20] = h + A[8];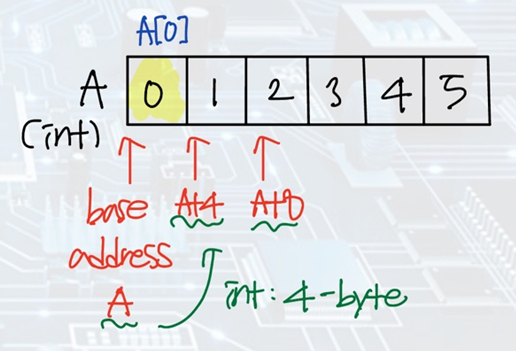
Register vs. Memory
- Registers are faster to access than memory.
- Operating on memory data requires loads and stores.
- Compiler must use registers for variables as much as possible.
Constant or Immediate Operand
- Many times, a program will use a constant in an operation.
addi x22, x22, 4 # x22 = x22 + 4
Summary: RISC-V Operands
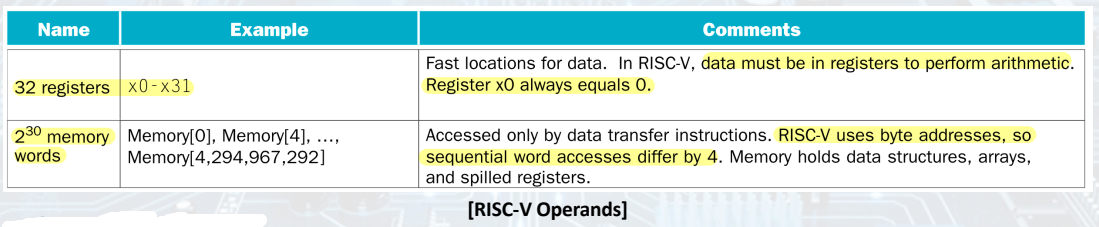
- 0~2^32 bytes --> 2^30 words
- 4 bytes = 1 word
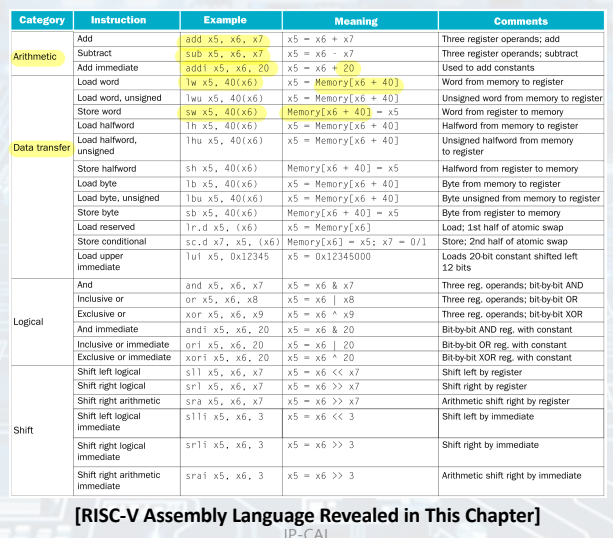
Summary: RISC-V Assembly Language
The Constant Zero
- RISC-V register x0($zero) is the constant 0.
--> Useful for common operations.
# Move between registers
add x2, x1, x0 # x2 = x1 + 0
Unsigned Numbers

2s-Complement Signed Integers

▶ Bit 31 is sign bit.
- 1: -
- 0: +

'Computer Architecture > 컴퓨터구조[05]' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [CA] Lecture #09 (0) | 2023.09.27 |
|---|---|
| [CA] Lecture #08 (0) | 2023.09.25 |
| [CA] Lecture #06 (0) | 2023.09.19 |
| [CA] Lecture #05 (0) | 2023.09.16 |
| [CA] Lecture #04 (0) | 2023.09.13 |



