Example 6
main:
li $s0, 0x06
li $s1, 0x10
move $a0, $s0 // $s0에서 $a0로 move
move $a1, $s1
jal sum
nop
move $s3, $v0 // Get the result
move $a0, $s3 // Print the sum
li $v0, 1
syscall
li $v0, 1 // Exit
syscall
sum:
add $t1m $a0, $a1
move $v0, $t1
jr $ra // Return to the main function
nop
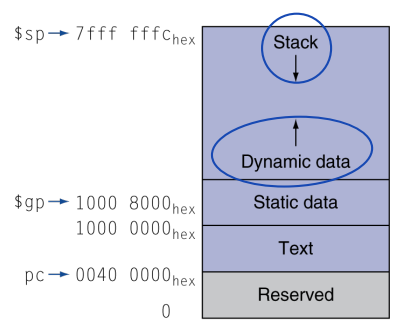
Memory Layout
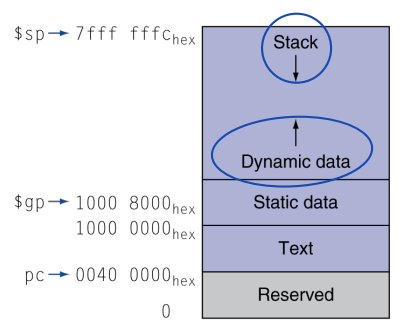
- Stack: automatic storage
- Dynamic data: heap
- Static data: global variable
- Text: program code
Jump Addressing
: j, jal
Jump targets could be anywhere in text segment.
Branching Far Away
: beq, bne
If branch target is too far to encode with 16-bit offset, assembler rewrite the code.
// Example
beq $s0, $s1, L1 // cannot reach L1 (가정)
bne $s0, $s1, L2
j L1 // jump 연산으로 변경한다.
- Branch: 16-bit 내에서 branch 가능
- Jump: 어디든 갈 수 있음
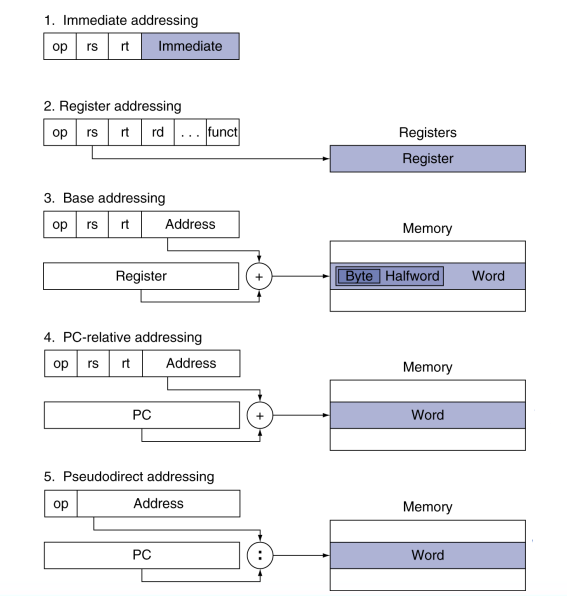
Addressing Mode Summary
Assembler Pseudo Instructions
- Pseudo instructions: Figments of the assembler's imagination.
- Native instructions
// move --> add
move $t0, $t1 // $t1에서 $t0로 move
add $t0, $zero, $t1 // $t0 = 0 + $t1blt --> slt, bne
blt $t0, $t1, L // if($t0 < $t1), branch to L
slt $at, $t0, $t1 // Set Less Than, if ($t0 < $t1), $at = 1
bne $at, $zero, L
Ch3: Logic and Arithmetic
Positional Notation of Numbers
- Binary numbers (2진수)
- Hexadecimal numbers (16진수)
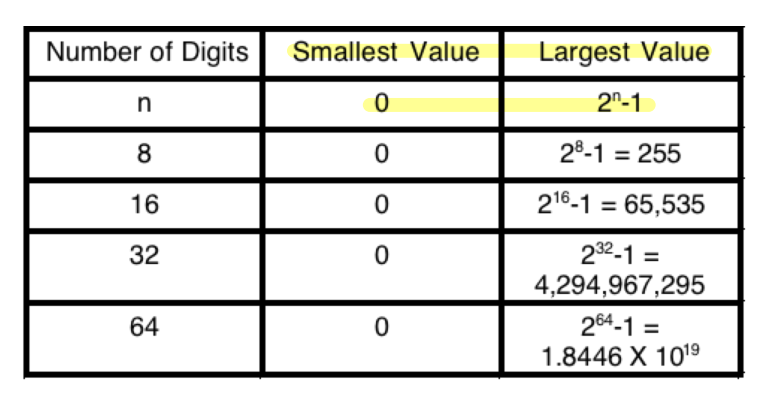
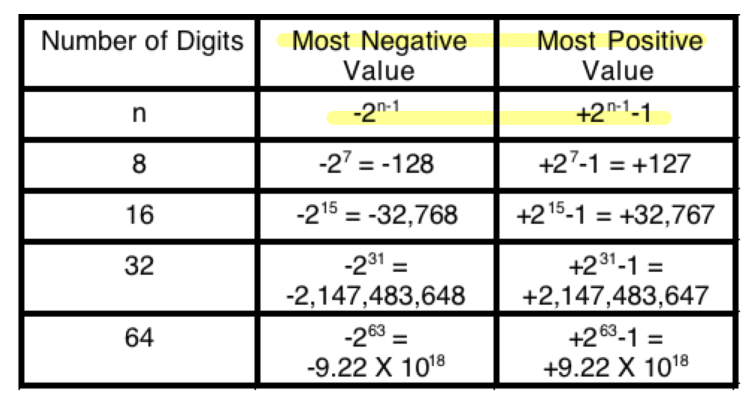
Range of Unsigned Binary Numbers
Unsigned vs. Signed Numbers
- unsigned int x;
- int x;
Signed Number Representations
1) Sign/Magnitude Representation

2) One's Complement Representation
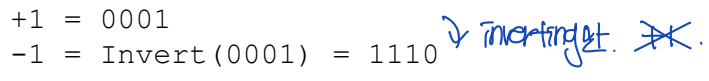
3) Biased
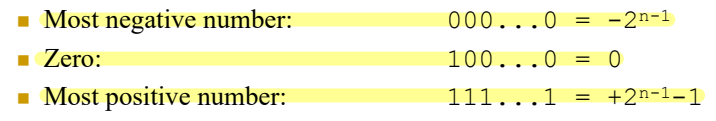
4) Two's Complement Representation
: 뒤집고, +1
Sign Extension
: Copy the sign bit.
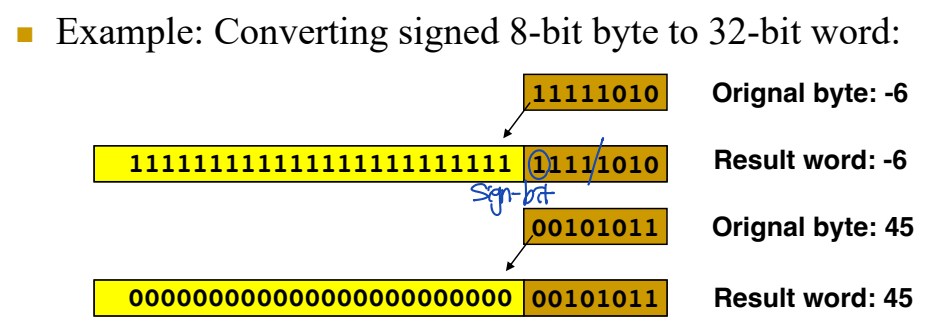
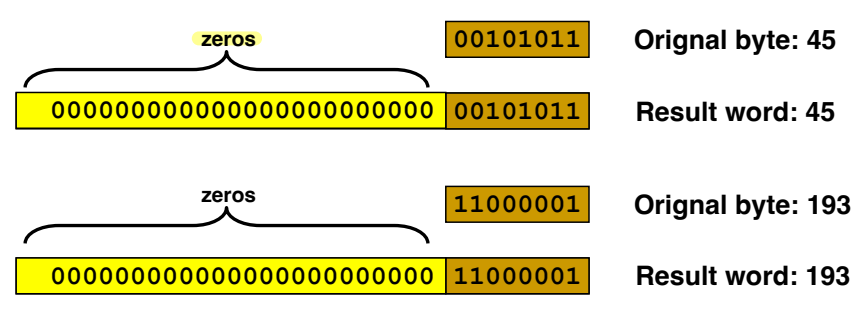
Zero-Padding for Unsigned Numbers
: Copy "zeros".
Sign Extension in MIPS
- Load-byte (lb) instruction: Loads an 8-bit signed number from memory to register.
- Load-byte unsigned (lbu) instruction: Loads an 8-bit unsigned number from memory to register.
Sign Extension in MIPS I-Format Instructions

- I-Format instruction --> 16-bit immediate field
- MIPS operations: defined on 32-bit registers. (MIPS 아키텍처에서 사용하는 레지스터는 32-bit 크기이다.)
--> Sign extension performed on immediate operands.
Signed & Unsigned Comparisons
- slt (Set Less Than): signed comparison
- sltu (Set Less Than Unsigned): unsigned comparison

--> 어떤 instruction을 쓰느냐에 따라 답이 달라질 수 있다.
Binary Addition
SBY 5-2
1. Write down an MIPS assembly code that gets two integers from a user console, and sums those values in a subroutine.
main:
li $v0, 5
syscall
move $s0, $v0 # the first read integer at $s0
li $v0, 5
syscall
move $s1, $v0 # the second read integer at $s1
move $a0, $s0
move $a1, $s1
jal sum_it
nop
# Get the result
move $s3, $v0
# Exit the program
li $v0, 10
syscall
sum_it:
add $t0, $a0, $a1
move $v0, $t0
jr $ra
nop
2. Can you draw the memory layout and specify what kind of data is stored at which area?
- Stack: automatic storage
- Dynamic data: heap
- Static data: global variable
- Text: program code
3. What are the main differences between branch addressing and jump addressing?
- Branch: I-format (constant address is 16-bit) --> 16-bit 내에서 branch할 수 있다.
--> PC-relative addressing: target address = PC + offset*4 - Jump: J-format (address is 26-bit) --> 멀리까지 jump할 수 있다.
--> Direct jump addressing

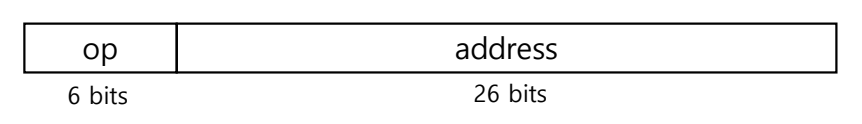
4. Represent -21 using 8-bit with 1) sign/magnitude, 2) one's complement, 3) two's complement.
- 10010101
- 11101010
- 11101011
'Computer Architecture > 컴퓨터구조[01]' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 2. 컴퓨터 언어 (0) | 2023.10.17 |
|---|---|
| [컴퓨터구조] 3. Arithmetic for Computers (2) (0) | 2023.10.09 |
| [컴퓨터구조] 2. Instructions: Language of the Computer (6) (0) | 2023.10.08 |
| [컴퓨터구조] 2. Instructions: Language of the Computer (5) (0) | 2023.09.27 |
| [컴퓨터구조] 2. Instructions: Language of the Computer (4) (1) | 2023.09.25 |


