Steps in Executing RISC-V
- IF: Instruction fetch from memory.
- ID: Instruction decode & register read. (어떤 instruction인지, register 값)
- EX: Execute operation (R-format), calculate address (lw, sw).
- MEM: Access memory operand.
- WB: Write result back to register.
Pipeline Performance
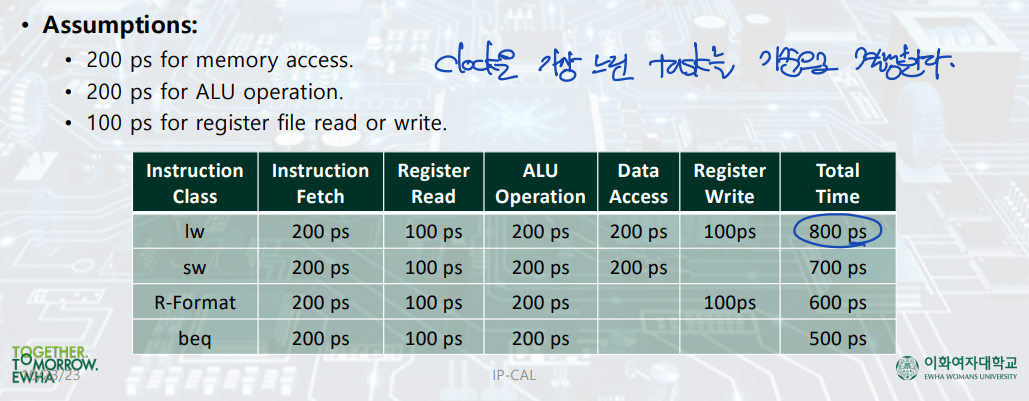
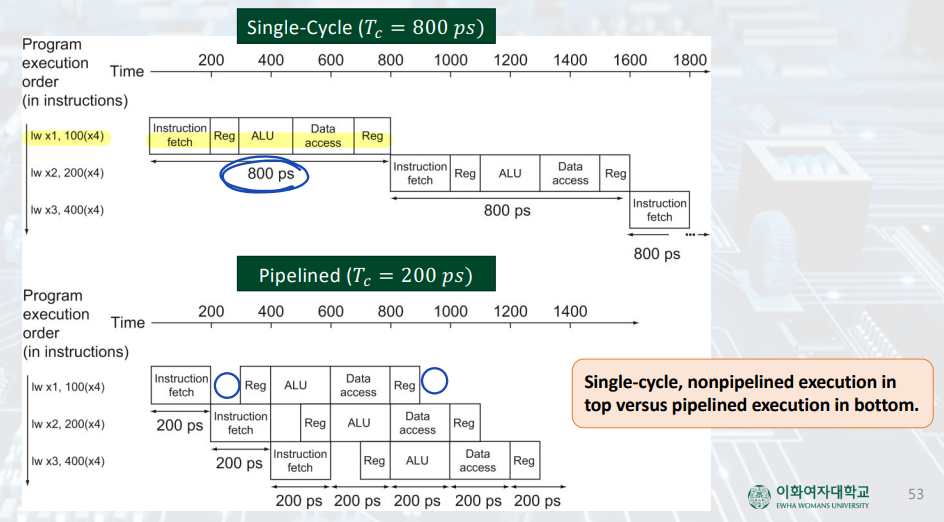
Ideal Speedup

: instruction의 단계를 동일한 시간으로 나눌 수 없기 때문에, 단계의 수 만큼 speed up 할 수는 없다.
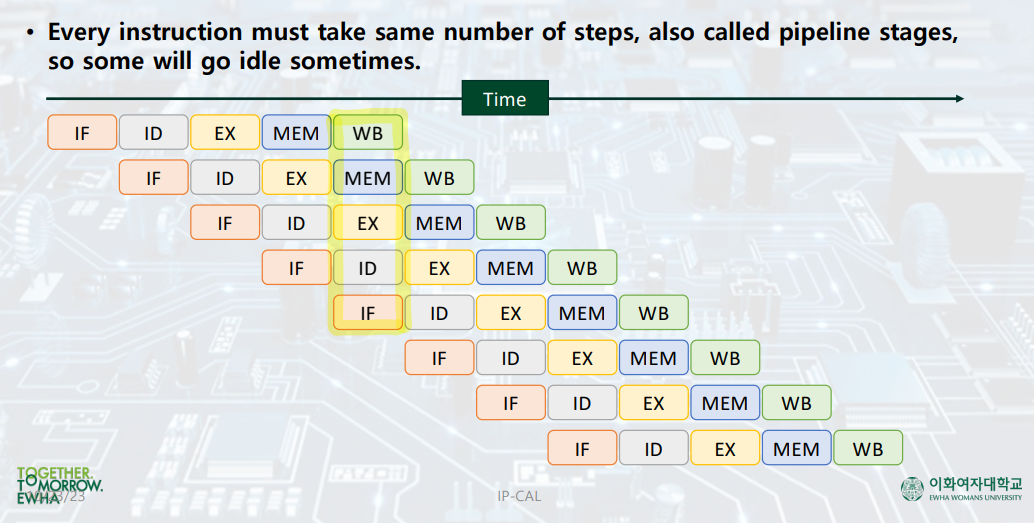
Pipelined Execution Representation
Review: Datapath for RISC-V

Hazards
: Hazards prevent next instruction from executing during its designated clock cycle.
- Structural hazard: A required resoruce is busy.
예) IF, MEM 동시에
예) WB, ID 동시에 - Data hazard: Need to wait for previous instruction to complete its data read/write.
- 앞선 연산의 destination이 바로 뒤 연산의 source가 된다면, WB단계가 완료되기 전에, ID를 할 수 없다. - Control hazard: Deciding on control action depends on previous instruction.
- branch 여부가 결정되어야 (EX 단계), 그 다음 연산의 수행 여부를 결정할 수 있다.
Structural Hazards
: Conflict for use of a resource.
- IF, MEM 동시에 --> Resource: memory
- WB, ID 동시에 --> Resource: register file
Structural Hazards: Single Memory

--> Solution: "Harvard architecture"
- IF: Instruction memory
- MEM: Data memory
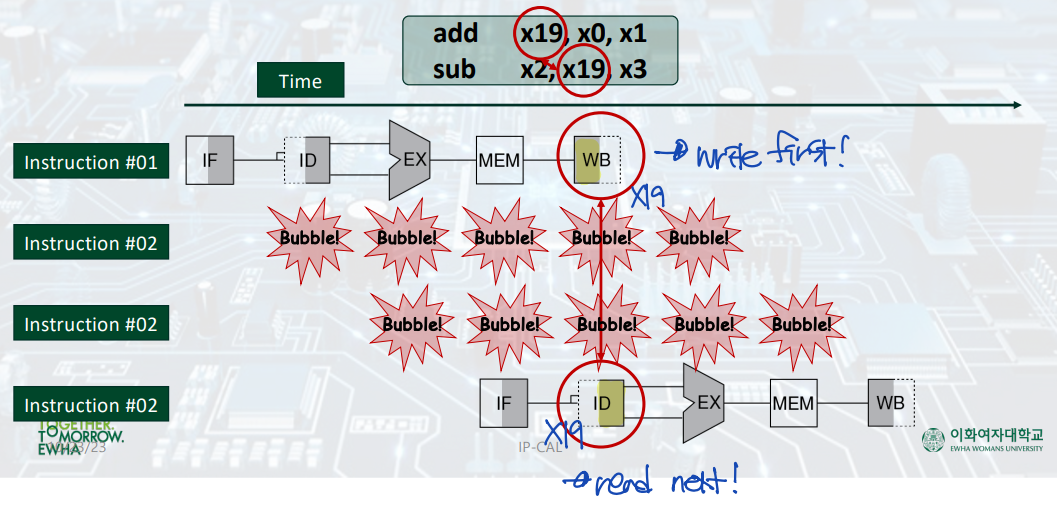
Structural Hazards: Registers

--> Solution: WB 먼저 (write first), ID 나중에 (read next)하면, correct data를 read할 수 있다.
Data Hazards
: An instruction depends on completion of data access by a precious instruction.
- 앞선 연산의 destination == 바로 뒤 연산의 source
--> Solution: forwarding or bypassing (pipeline register)
Forwarding with Two Instructions

: EX 단계가 끝난 후, 그 결과를 WB을 통해 destination register에 저장하기 전에, pipeline register를 통해 그 다음 연산의 EX 단계로 넣어준다.
Load-Use Data Hazard
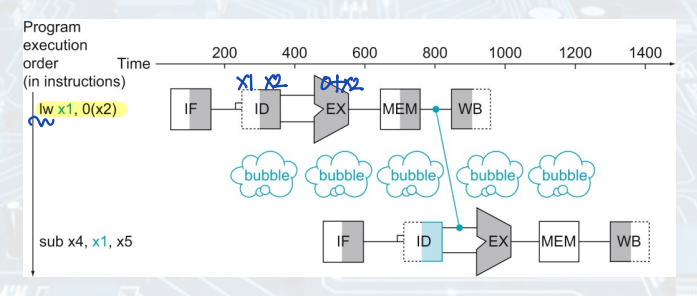
: lw와 같은 경우에, EX 단계 이후 MEM 단계에서 메모리에서 값을 읽어와야 하기 때문에, 1 clock cycle waiting은 필연적이다.
Code Scheduling to Avoid Stalls
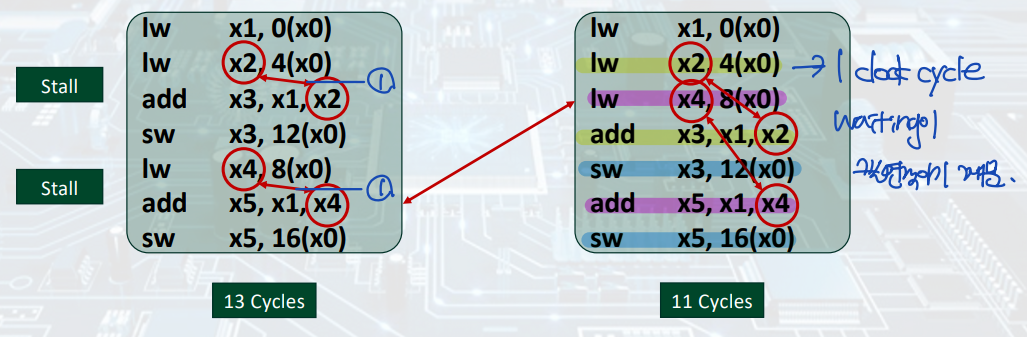
: 코드 순서를 변경하여, lw/sw에서의 필연적인 stall 문제를 해결할 수 있다.
Control Hazards

: Branch 할 지 여부를 결정하고 난 후 (EX 단계), 그 다음 instruction의 수행 여부를 결정할 수 있다. --> 1 bubble
Possible Solution: Branch Prediction
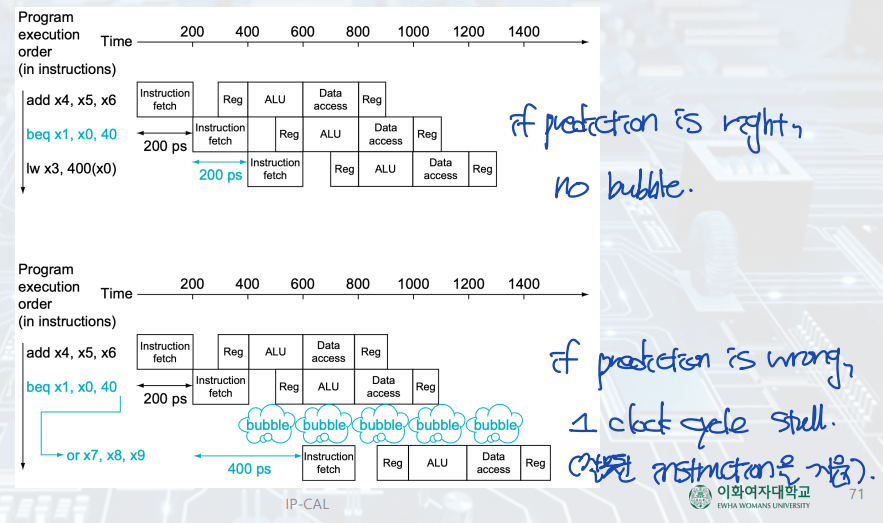
Dynamic Branch Prediction
: 이전의 branch 여부대로 predict한다.
- Keeping a history for each branch as taken or untaken, and then using the past to predict the future.
출처: 이화여자대학교 윤명국교수님 컴퓨터구조
'Computer Architecture > 컴퓨터구조[05]' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [CA] Lecture #21 (1) | 2023.11.15 |
|---|---|
| [CA] Lecture #20 (1) | 2023.11.14 |
| [CA] Lecture #18 (0) | 2023.11.08 |
| [CA] Lecture #17 (0) | 2023.11.07 |
| [CA] Lecture #16 - Ch4: The Processor (0) | 2023.11.05 |



