Interconnecting Components
: CPU, memory, I/O device controller 사이의 interconnection이 필요하다.
- Bus: Parallel set of wires for data and synchronization of data transfer.
--> 성능은 물리적 요인의 제약을 받는다.
Bus Types
▶ Processor-Memory buses: CPU와 memory를 연결해주는 버스
=> Main memory --> bus --> north bridge --> bus --> CPU
- Short, high speed
▶ I/O buses: Processor-Memory bus와 I/O device를 연결해주는 버스
=> Disk --> bus --> south bridge --> bus --> north bridge --> bus --> Main memory, CPU
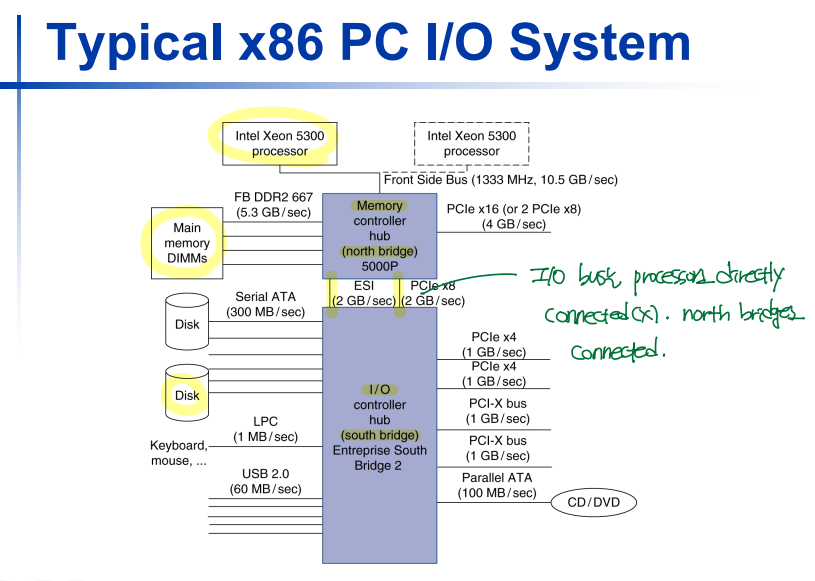
I/O Bus Examples

I/O Management
- Multiple programs share I/O resources.
- I/O causes asynchronous interrupts.
I/O Commands
: I/O device는 device controller라는 하드웨어에 의해 관리된다.
- CPU -- device controller -- I/O device
--> device controller를 통해 CPU와 I/O device가 서로 데이터를 전송한다.
▶ Device controller
- Command register: CPU가 I/O device에게 명령하도록 하는 레지스터
- Status register: I/O device의 상태를 표시하는 레지스터
- Data register
- Write: transfer data to a device
- Read: transfer data from device
Q. 그렇다면, CPU는 device controller의 이러한 레지스터들에 어떻게 접근할까?
- Memory mapped I/O
- I/O instructions (= Isolated I/O)
I/O Register Mapping
Memory mapped I/O
: I/O device에 접근하는 device controller 내의 레지스터들에 대한 주소가, 메모리 주소와 유사한 형태로 작성된다.
--> CPU가 device controller의 레지스터에 접근할 때, 메모리에 접근할 때와 동일한 방식으로 접근하면 된다.
- Address decoder: 메모리 주소와 device controller의 레지스터 주소를 구분해준다.
Device controller의 레지스터에 접근한다는 것은 I/O device에 대한 통제권을 갖는다는 것이다. 따라서 OS는 device controller의 레지스터에 대한 주소 변환 매커니즘을 커널만이 접근할 수 있도록 한다.
I/O instructions (= Isolated I/O)
: I/O device에 접근하는 device controller 내의 레지스터들에 대한 주소와, 메모리 주소가 서로 다른 형태로 작성된다.
Q. 그렇다면, I/O device와 CPU는 어떻게 소통할 수 있을까?
- Polling
- Interrupts
I/O Data Transfer
Polling
: CPU가 주기적으로 device controller의 state register 상태를 체크한다.
--> If device ready, do operation.
--> If error, take action.
- Common in small or low-performance real-time embedded systems.
- Predictable timing
- Low hardware cost (Interrupt handler 하드웨어가 필요하지 않다.) - In other systems, wastes CPU time. (CPU가 계속 device controller의 레지스터 상태를 확인하고 있어야 하기 때문이다.)
Interrupts
: I/O device가 입출력 작업을 수행하다가 작업이 완료되면, device controller가 CPU에 인터럽트를 걸어서 알려준다.
▶ Interrupt:
- Not synchronized to instruction execution. (clock과 상관없이 아무때나 발생할 수 있다.)
- 인터럽트가 발생하면, PC가 interrupt handler 주소를 가리키고, interrupt handler가 인터럽트를 처리한다.
▶ Priority interrupts
: I/O device와 device controller가 많을 때는, 인터럽트 여러 개가 발생할 수 있다.
--> 우선순위에 따라 처리한다.
Direct memory access (DMA)
▷ Problem: Polling과 Interrupt 방식의 문제점은, CPU가 항상 device controller의 레지스터와 memory 사이의 데이터 전송에 끼어 있다는 것이다.
- Device controller의 데이터를 먼저 CPU의 레지스터에 적재하고, 메모리에서 CPU의 레지스터에 접근하여 그 데이터를 읽어간다.
- 메모리의 데이터를 먼저 CPU의 레지스터에 적재하고, device controller에서 CPU의 레지스터에 접근하여 그 데이터를 읽어간다.
▶ Solution: DMA(Direct Memory Access)
: Device controller와 메모리가 CPU를 거치지 않고 직접 연결되도록 한다!
- Device controller: CPU의 역할을 대신 수행한다.
- CPU가 device controller에게 메모리 주소를 제공한다. (device controller와 메모리가 직접 연결될 수 있도록!)
- Device controller가 메모리와 직접 연결된다.
- I/O device의 입출력 작업이 완료되면, device controller에서 CPU에게 인터럽트를 걸어서, 작업 완료를 알린다.
♧ 정리하자면 !!
- Polling: CPU가 device controller를 항상 들여다보고 있다가, device가 준비가 되면, device controller와 소통한다.
- Interrupt: I/O device --> device controller에서 인터럽트를 발생시키면, CPU가 device controller와 소통한다.
이때 CPU는 device controller의 레지스터들에게 접근하기 위해,
- Memory mapped I/O
- I/O instructions (= Isolated I/O)
방식을 이용한다.
- DMA: I/O device --> device controller는 CPU를 거치지 않고, 메모리와 직접 소통한다.
Q. DMA(Direct Memory Access) 방법을 이용하면, CPU는 device controller에게 자신의 일을 넘기고, 따라서 device controller의 레지스터와 메모리 사이의 소통에 CPU가 끼어들지 않게 된다. 그렇다면 DMA 방식을 이용하면, CPU가 device controller의 레지스터들에게 접근하지 않으니, memory mapped I/O 방식과 I/O instruction 방식 모두 이용하지 않게 되는 것인가?
A. No! Device controller가 CPU를 대신해서 처리하니, device controller의 레지스터와 메모리가 memory mapped I/O를 이용하게 된다. 정리하면,
- Polling, Interrupt: device controller register들이 메모리에 접근하고자 할 때, CPU를 거친다. 메모리가 device controller register들에 접근하고자 할 때, CPU를 거친다. 따라서 CPU가 device controller에게 접근해주어야 하는데, 이때 memory mapped I/O 방식을 이용하면 CPU는 device controller에 대한 주소를 마치 메모리 주소처럼 생각하면 되고, I/O instructions 방식을 이용하면 CPU는 device controller에 대한 주소를 메모리 주소와는 다른 형식으로 생각해야 한다.
- DMA: device controller와 메모리가 소통할 때, CPU를 거치지 않고 직접 소통한다. 이때, device controller와 CPU가 소통하지 않는다고 해서 device controller에 접근할 필요가 없어지는게 아니다. 메모리가 device controller에게 접근한다. 메모리는 device controller에게 접근할 때 memory mapped I/O를 이용한다.
DMA/Cache Interaction
DMA(Direct Memory Access) 방식에서는 device controller와 memory 간의 데이터 전송에서 CPU가 빠지게 된다. CPU는 device controller에게 memory 주소를 알려주기 때문에, 굳이 개입할 필요가 없다.
'device controller --> CPU (+ cache) --> memory' 이렇게 중간에 CPU를 거치는 방법에서는 cache도 함께 거쳤다. 따라서 이때는 device controller가 원하는 주소를 굳이 memory에 접근할 필요 없이, cache에서 얻을 수 있었다. 또 반대로, device controller는 memory에 쓸 주소를 cache에 미리 써놓기도 했다.
- Probelm: 그런데 갑자기 device controller가 CPU와 cache를 거치지 않고 바로 memory로 접근하게 한다면?!
Write-back cache가 dirty block을 갖고 있었다면, 즉 아직 cache에서 쫓겨나지 않았기 때문에 memory에는 업데이트되지 않고 cache에만 쓰인 데이터가 있었다면?!
--> Device controller는 cache를 거치지 않고 memory로 접근하기 때문에 업데이트되지 않은 정보를 얻게 된다. (Device controller reads stale data.)
--> Needs to ensure cache coherence!
- Solution 1) Flush blocks from cache if they will be used for DMA (device controller).
- Solution 2) Use non-cachable memory locations for I/O. (아예 캐시를 처음부터 쓰지 않도록 한다.)
DMA/VM Interaction
DMA(Direct Memory Access) 방식에서는 device controller가 CPU로부터 memory 주소를 받고, CPU를 거치지 않은 채 memory와 직접 소통한다. 따라서 DMA 방식을 이용할 때는 하나의 프로그램에 대한 memory 주소가 서로 떨어져 있으면 안 된다.
- Problem: Device controller가 CPU로부터 제공받는 memory 주소는 virtual memory 주소이다. 즉, 같은 프로그램에 대해 virtual memory address는 서로 붙어 있을지라도, physical memory에서는 서로 떨어져 있을 수 있다.
- Solution 1) DMA가 virtual address를 이용하도록 한다면, device controller should do the translation.
- Solution 2) DMA가 physical address만을 이용하도록 한다면, device controller에서 memory로의 전송을 page 단위로 나눠서, 적어도 page 단위에서는 physical memory address가 연속적이게 되도록 해야 한다.
Q. DMA 방식을 이용할 때는 하나의 프로그램에 대한 physical memory 주소가 서로 떨어져 있으면 안 되는 이유가 무엇인가요? Virtual memory를 이용하면, virtual memory address에 대응되는 physical memory address는 떨어져 있을 수 있습니다. 그런데 DMA(Direct memory access) 즉 device controller와 메모리가 직접 소통하는 방식에서는 physical memory address가 서로 붙어있어야 하는 이유가 있나요?A. DMA는 device controller와 메모리 사이에서 데이터를 빠르게 전송하기 위해 사용되는 것인데, physical memory address가 여기저기에 떨어져 있으면 device controller가 메모리에 데이터를 복사하기 위해 접근하는 시간이 오래 걸린다. 최대한 빠르게 데이터 전송을 하기 위해서는, 지금 start memory address와 end memory address가 연속되어 있는 것이 좋다.Virtual memory를 이용하면 physical memory address가 떨어져 있을테니, virtual memory를 이용할 때 page table이나 TLB를 이용하여 주소 변환을 하는 것은 당연한거고, virtual memory를 이용하지 않더라도 physical memory address가 붙어 있어야 한다는 이야기를 하는 것이다.
Virtual memory를 이용하지 않을 때는, 주소 변환은 필요하지 않지만, physical memory address가 붙어있도록 하는 것이 좋다. 만약 이게 현실적으로 불가능하다면, 메모리를 page 단위로 쪼개서, 적어도 page 단위에서는 physical memory address가 붙어있도록 한다. 이렇게 하면, DMA(Direct Memory Access)의 효과를 최대로 낼 수가 있다.
I/O vs. CPU Performance
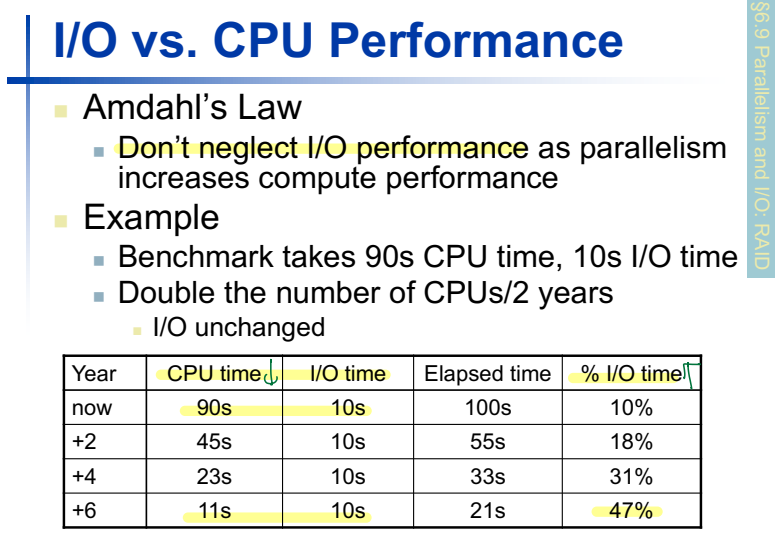
: CPU time의 발전에 비해 I/O time의 발전은 더디게 일어났다. 따라서 I/O time은 전체 시간에서 매우 큰 비중을 차지한다.
RAID (Rebundant Array of Inexpensive Disks)
: 하나의 큰 disk 대신 작고 많은 disk를 이용한다.
- 병렬성은 성능을 향상시킨다.
- Fault tolerant storage system
RAID 0
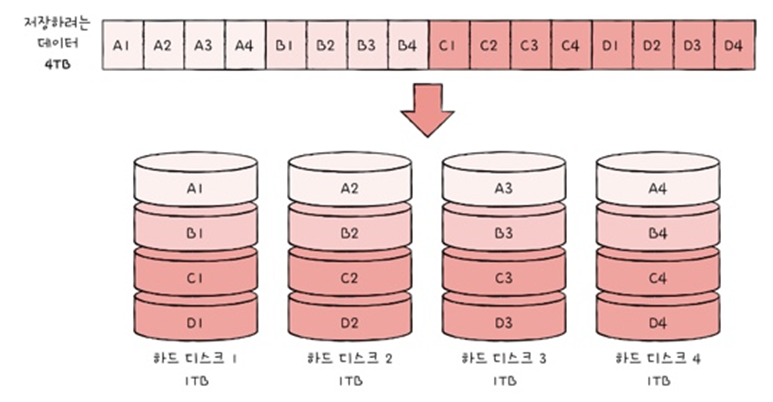
: 여러 개의 disk에 단순히 나눠서 저장하는 저장 방식
RAID 1
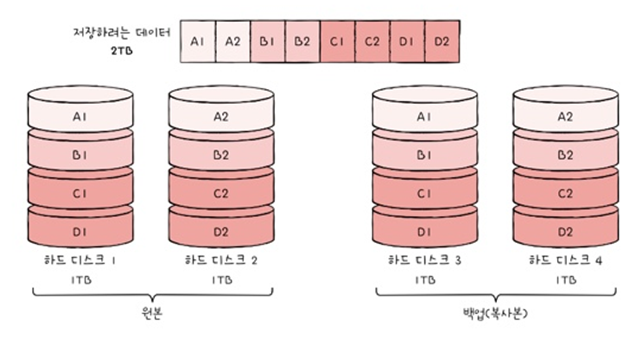
: 복사본을 만드는 방식 (mirroring)
- Write data to both data disk and mirror disk.
RAID 2
: N개의 main disk와 E개의 error correcting disk를 두는 방식
- main disk: 데이터를 N개의 disk로 나눈다.
- ECC(Error correcting code): E-bit를 통해 에러를 확인한다. (예: parity)
RAID 3
: N개의 main disk와 1개의 parity disk를 두는 방식 (RAID 2와 달리, error correcting에는 항상 parity bit을 이용한다.)
- Data striped accross N disks at byte level.
- Read access: Read all disks.
- Write access: Generate new parity and update all disks.
- Use parity to reconstruct missing data.
RAID 4
: N개의 main disk와 1개의 parity disk를 두는 방식
- Data striped accross N disks at block level.
- Read access: Read only the disk holding the required block. (Block-level이기 때문!)
- Write access: Calculate new parity, update data disk and parity disk.
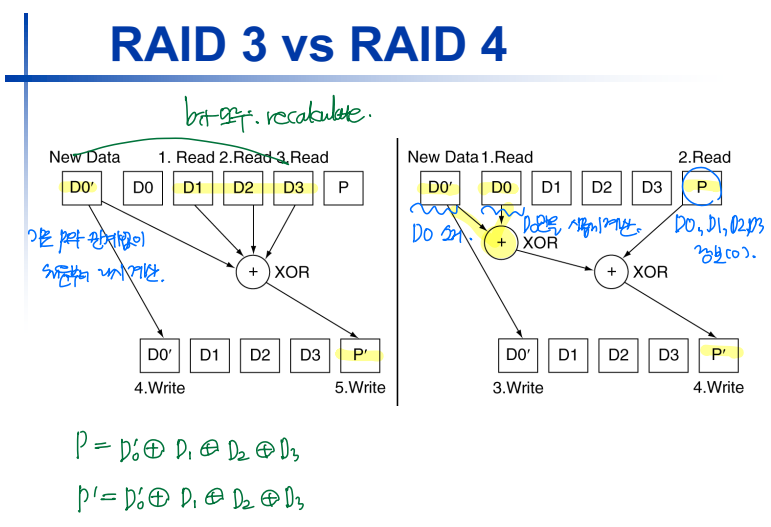
- RAID 3: byte level이기 때문에, 기존의 parity 값과 상관없이 새로운 parity를 계산한다.
- RAID 4: block level이기 때문에, 기존의 parity 값에서 필요없는 부분을 소거한 후, 새로운 parity를 계산할 때는 필요한 부분만 추가한다.
출처: 이화여자대학교 이형준교수님 컴퓨터구조
'Computer Architecture > 컴퓨터구조[01]' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [컴퓨터구조] 1206 (2) (2) | 2023.12.06 |
|---|---|
| [컴퓨터구조] 1206 (1) (0) | 2023.12.06 |
| [혼자 공부하는 컴퓨터구조] 07-2. RAID의 정의와 종류 (1) | 2023.12.04 |
| [혼자 공부하는 컴퓨터구조] 08-2. 다양한 입출력 방법 (1) | 2023.12.04 |
| [혼자 공부하는 컴퓨터구조] 08-1. 장치 컨트롤러와 장치 드라이버 (1) | 2023.12.04 |



