Ch5: Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy
Memory Hierarchy

--> Processor에 가까워질수록 작아지고, 빨라진다.
Principle of Locality
- Temporal locality: Items accessed recently are likely to be accessed again soon. (예: instructions in a Loop)
- Spatial locality: Items near those accessed recently are likely to be accessed soon. (예: sequential instructions)
--> Cache에는 Locality가 있는 데이터를 저장한다.
Memory Hierarchy Organization

- Processor <-> Memory: 4B (by. lw, sw)
- Processor <-> Cache: 4B
- Cache <-> Memory: 64B 또는 32B (Block 단위로 transfer)
Some Terminologies
- Block: the minimum unit of information.
- Hit --> Hit Rate
- Miss --> Miss Rate
- Hit time: 메모리 계층구조의 upper level에 접근하는 시간
- Miss penalty: 캐시 미스가 발생했을 때, 메모리 계층구조의 upper level block을 lower level의 다른 block으로 대체하는 시간 + 이 대체된 block을 processor로 이동하는 시간
The Basics of Caches
- L1 cache
- L2 cache
- L3 cache
DRAM Technology
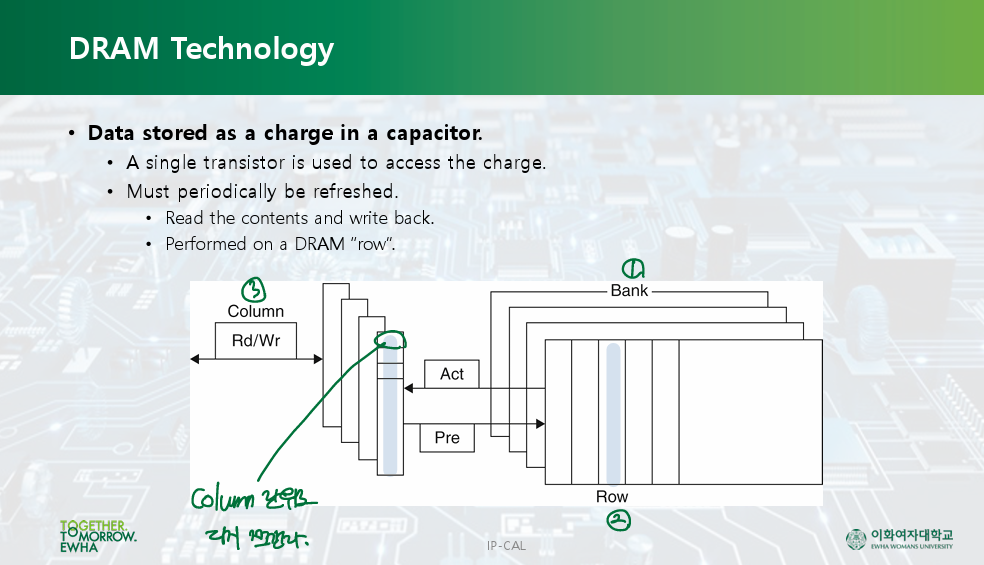
- SRAM, DRAM: volatile memory
Flash Storage
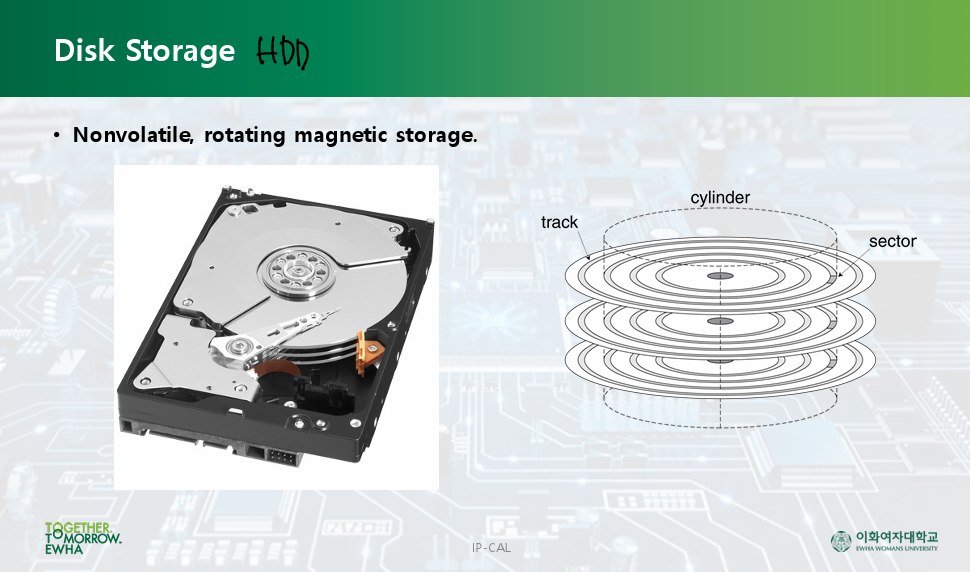
Disk Storage: HDD
Cache Memory
: The level of the memory hierarchy closest to the CPU.
Direct Mapped Cache

- Cache entry: 8개 (3-bit)
- Memory entry: 32개 (5-bit)
--> Memory entry들의 하위 3-bit를 Cache entry와 매칭시킨다.
- Tag: 하위 3-bit 이외의 나머지 비트 --> 하나의 Cache entry에서 각각의 Memory entry를 구분한다.
▷ 1개의 Cache entry 당 1개의 room이 있다. (Only one choice!)
Tags and Valid Bit
- Index: 캐시 엔트리 인덱스
- V(valid bit): 캐시 엔트리에 데이터가 들어있는지 알려주는 비트
- Tag: Index + Tag = 전체 메모리 주소 --> 메모리 엔트리를 구분할 수 있도록 하는 비트들
- Data: 메모리에서 가져온 데이터
Cache Example

- 원하는 메모리 주소에 맞는 Index를 찾는다.
- 그 Index의 valid bit을 보고, 데이터가 있는지 확인한다.
- 만약 데이터가 없다면, Cache Miss (called miss; 아무것도 없어서 데이터를 복사해오는 것)
- 만약 데이터가 있다면,
- Tag까지 매칭된다면: Cache Hit!
- Tag가 다르다면: Cache Miss (complete miss; 대체하는 것)
Address Subdivision
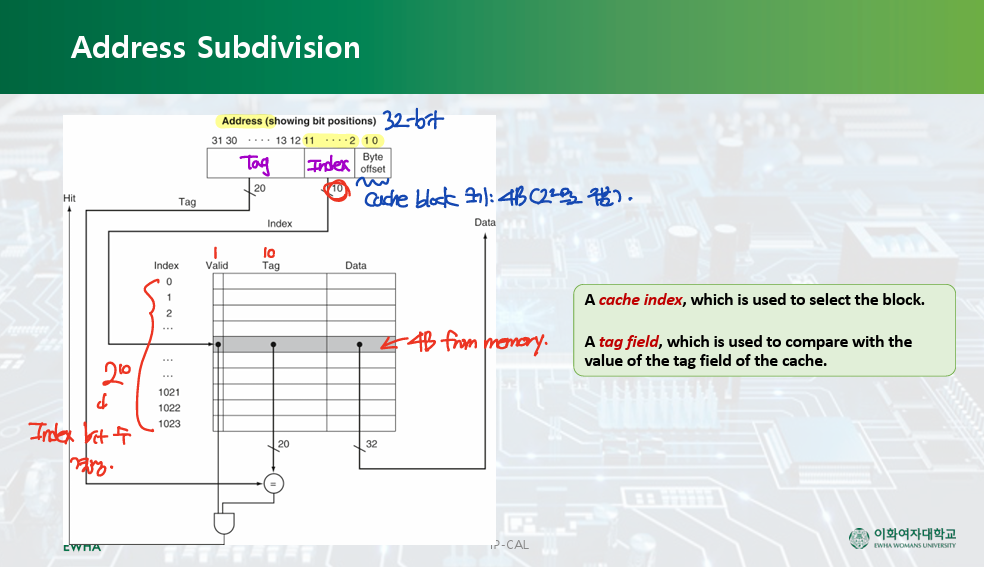
- Byte offset: 메모리에서 가져올 데이터가 4B이기 때문에, 이 데이터를 구분하기 위해 2-bit가 필요하다.
- Index: 총 캐시 주소가 2^10개이기 때문에, 주소를 구분하기 위해 10-bit가 필요하다.
- Tag: 나머지 (32-bit - Byte offset - Index)
출처: 이화여자대학교 윤명국교수님 컴퓨터구조
'Computer Architecture > 컴퓨터구조[05]' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [CA] Lecture #25 (1) | 2023.11.28 |
|---|---|
| [CA] Lecture #24 (0) | 2023.11.23 |
| 파이프라이닝(Pipelining)과 비순차적 명령어 처리(Out-of-order execution) (3) | 2023.11.20 |
| [CA] Lecture #22 (1) | 2023.11.17 |
| [CA] Lecture #21 (1) | 2023.11.15 |



