Overview
▶ Both hardware and software affect program performance
- Algorithm --> number of source-level statements.
- Language/Compiler/Architecture --> the number of machine instructions.
- Processor/Memory --> how fast instructions are executed.
- I/O system (hardware and OS) --> how fast I/O operations are executed.
Classes of Computer Systems
Desktop Computer Systems
▶ For "General-Purpose" Use
▶ What's in the box?
- Microprocessor
- Memory - Synchronous DRAM
- HHD, CDROM/DVD ...etc
- I/O: mouse, keyboard, video card, monitor, network ...etc
▶ Important Issues:
- Performance
- Basic capabilitis, expandability
- Cost
Server Computer Systems
▶ Large-Scale Services
- File storage
- Computation (ex. supercomputers)
- Transaction processing, Web
▶ What's in the box?
- Microprocessor
- HDD
- Network interface
▶ Important Issues:
- Performance
- Reliability, availability
- Cost
Embedded Computer Systems
▶ Computer as part of larger system
- Consumer electronics, appliances
- Networking, telecommunications
- Automotive / aircraft control(항공기 제어)
▶ What's in the box?
- Microcontroller, Microprocessor
- Memory: RAM(Random Access Memory), ROM(Read Only Memory), Disk
- Special-purpose I/O
▶ Important Issues:
- Performance
- Reliability, Safety
- Cost, Power consumption
Computer System Organization
▶ Five Classic Componenets
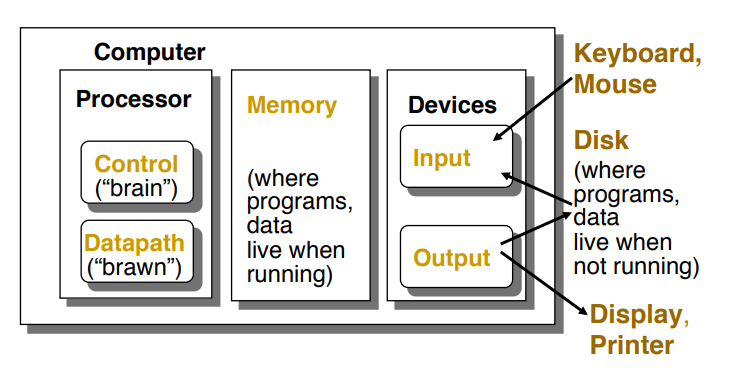
- Processor(CPU)
- Control: 프로그램의 명령어에 따라 데이터패스, 메모리, 입출력 장치에 지시를 한다.
- Datapath: 산술/논리 연산을 수행한다. - Memory
- Devices
- Input
- Output
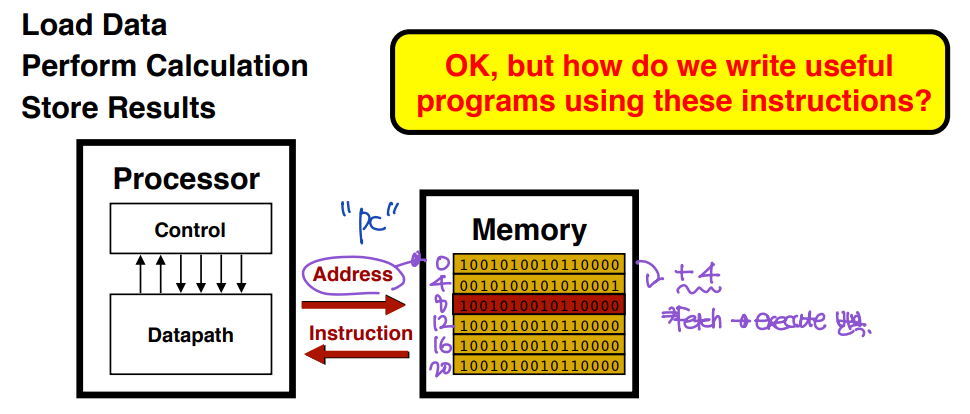
▶ Executing Programs - the "fetch/execute" cycle
- Processor fetches instruction from memory.
- Processor executes "machine language" instruction.
Abstractions in Computer Systems
: Designers use abstraction to manage complexity

Software Abstractions - Languages
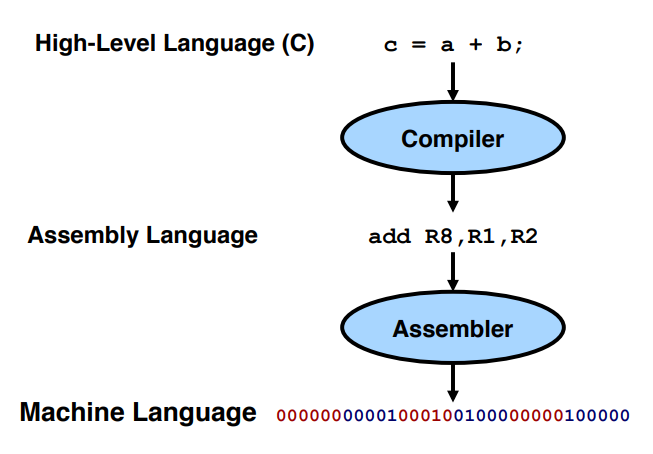
Software Abstractions - System Software
▶ Operating System
- Programs interact with OS through system calls.
▶ Libraries
- Programs access through well-defined interfaces. (API; Application Programming Interface)
ISA(Instruction Set Architecture) - The Hardware-Software Interface
: The most important abstraction of computer design.
- ex. MIPS
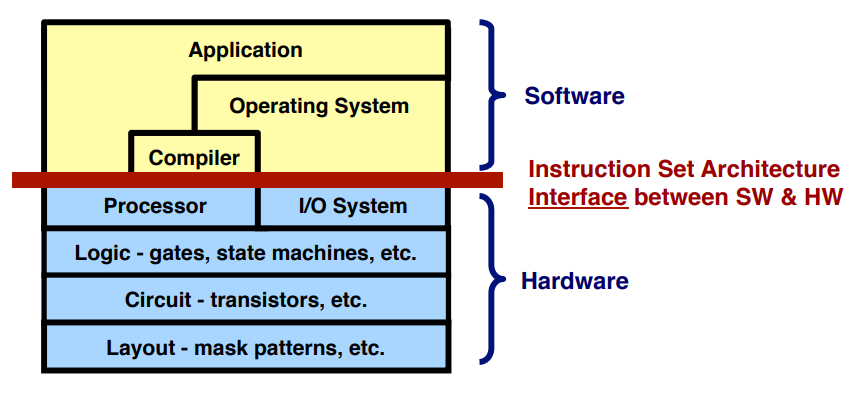
ISA(Instruction Set Architecture)
▶ A very important abstraction
- Interface between hardware and low-level software.
- Included: instructions, registers, memory access, I/O ...
- Advantage: different implementations of the same architecture.
- Disadvantage: sometimes prevents using new innovations.
Architecture vs. Organization
- Architecture: features visible to programmer.
- Organization: system implementation.
Example Architecture: MIPS

Overview of Physical Implementations
- Integrated Circuits (ICs)
: Combinational logic circuits, memory elements, analog interfaces. - Printed Circuit Boards (PCB) = Main Board
: Substrate(구성요소) for ICs and interconnection, distribution of CLK(clock), Vdd, GND signals, heat dissipation. - Power Suppliers
- Chassis
- Connectors and Cables
Organization of a Desktop PC
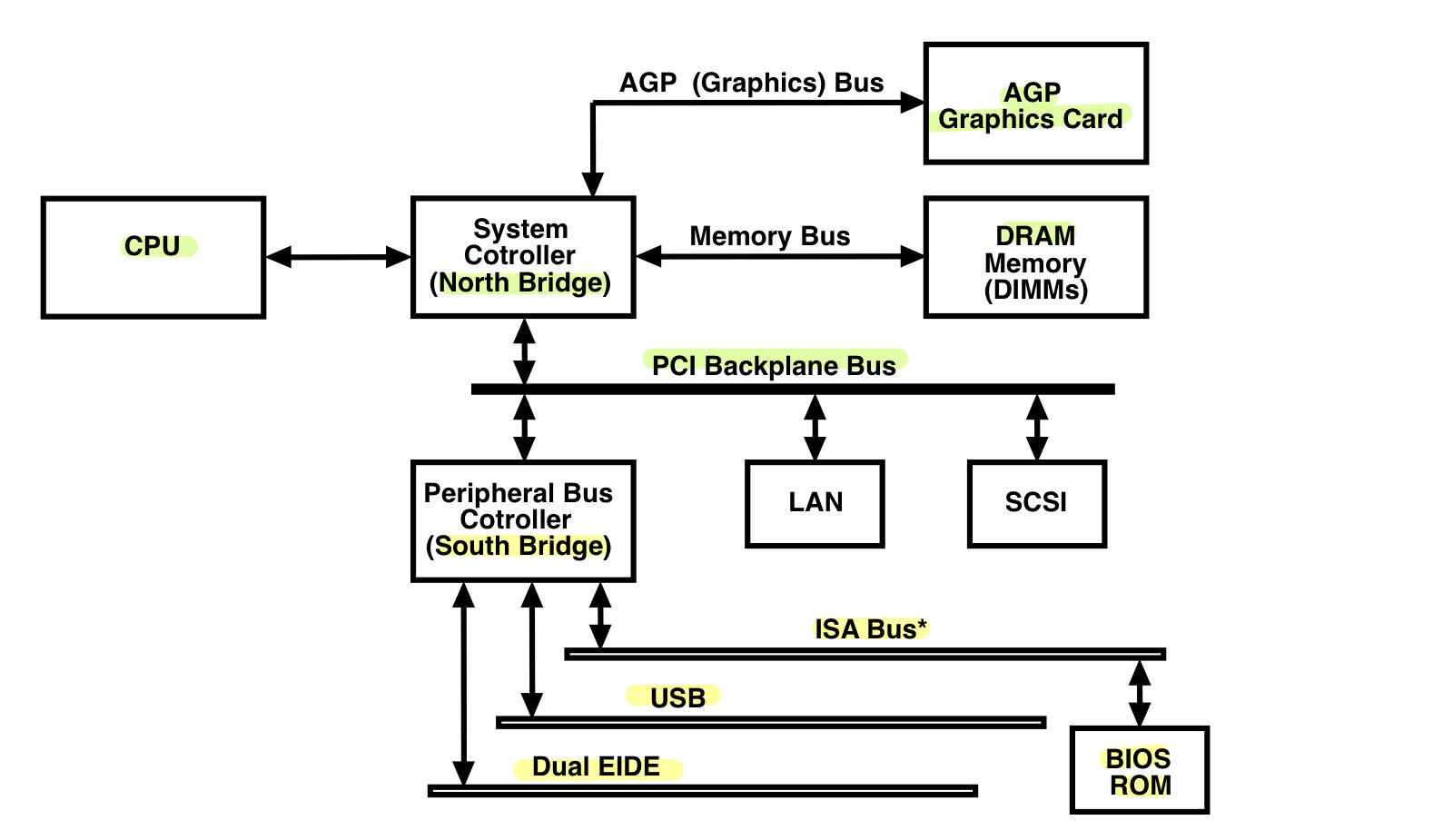
- System Controller - North Bridge
: A chip that connect a CPU to memory, the PCI bus, Level 2 cache and AGP activities. - Peripheral(주변적인) Bus Controller - South Bridge
: A chip that controls all of the computers I/O functions such as USB, audio, serial, the system BIOS, the ISA bus, the interrupt controller and IDE channels. - IDE(Intelligent(지능형) Drive Electronics) interface
: An interface for mass storage devices, in which the controller is integrated into the disk or CD-ROM drive. - PCI(Peripheral Component Interconnect)
: A local bus standard developed by Intel Coperation.
- Most modern PCs include a PCI bus in addition to a more general ISA expansion bus. - AGP(Accellerated Graphics Port)
: An interface specification(사양) developed by Intel Corporation.
- AGP is based on PCI, but is designed especially for the throughput demands of 3D graphics. - Industry Standard Architecture bus
: A bus architecture used in the IBM PC/XT and PC/AT.
Typical Motherboard
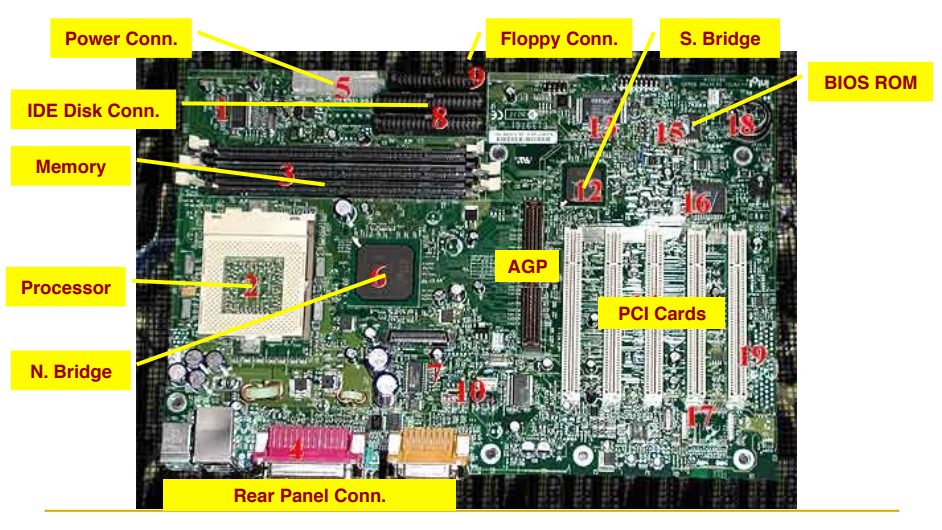
SBY 1-2
1. What are five components in computer system?
▶ CPU
- Control unit: CPU의 brain, 프로그램의 명령어에 따라 Datapath, Memory, I/O device에 지시를 한다.
- Datapath: 산술/논리 연산을 수행한다.
▶ Memory: 실행 중인 프로그램과 프로그램 실행에 필요한 데이터를 저장한다.
▶ I/O devices
- Input device: 외부 환경에서 정보를 수집하고, 컴퓨터 시스템이 그 정보를 처리하도록 전달한다. 예) 키보드, 마우스
- Output device: 컴퓨터에서 생성된 정보 등의 결과를 사용자에게 표시하거나 출력한다. 예) 프린터
Cf) Disk: 디스크는 데이터의 읽기와 쓰기가 모두 가능하기 때문에 input device와 output device 모두로 사용된다.
- 데이터 읽기 (Input): 디스크는 저장된 데이터를 읽어오는 데 사용됩니다. 예를 들어, 컴퓨터의 하드 디스크 드라이브는 저장된 파일, 문서, 음악, 비디오 및 기타 정보를 읽어오는 데 사용됩니다. 데이터를 디스크에서 읽어와 메모리로 전송하여 프로그램이나 응용 소프트웨어에서 처리할 수 있습니다.
- 데이터 쓰기 (Output): 디스크는 데이터를 저장하고 기록하는 데 사용됩니다. 사용자가 파일을 작성하거나 수정하면 컴퓨터는 해당 데이터를 디스크에 쓰고 저장합니다. 디스크는 데이터를 저장 매체에 기록하므로 나중에 읽어오거나 다시 사용할 수 있습니다.
2. Can you explain the procedure of "executing programs" with some illustrative(실례가 되는) figures?
- 사용자가 프로그램을 작성한다.
- 컴파일러가 프로그램을 기계어로 변환한다.
- 프로그램이 메모리로 로드(load)된다.
메모리는 주기억장치(RAM; Random Access Memory)로서, 데이터와 프로그램의 명령어를 저장하는 공간이다. - CPU가 명령어를 메모리에서 가져와서(fetch) 해당 명령어를 해석하고, 실행(execute)한다.
: CPU fetches insturction from memory and executes machine language instruction.
이때, CPU의 Register 중 하나인 PC(Program Counter)는 현재 실행중인 명령어어의 Address를 가리킨다. CPU는 PC의 Address에 따라 다음 번에 실행할 명령어의 Memory address를 결정한다. 명령어를 실행할 때마다 PC의 값이 4씩 증가하고, 다음 명령어의 Address로 업데이트 된다. - 프로그램 실행이 완료되면 결과가 output device에 출력된다.
3. Which factors in hardware and software affect program performance?
- Algorithm --> 알고리즘은 source-level statement의 수를 결정한다.
- Language/Compiler/Computer architecture --> 언어, 컴파일러, 컴퓨터 구조는 기계어 수를 결정한다.
- Processor/Memory --> 프로세서, 메모리는 명령어들이 어떻게 수행될지를 결정한다.
- I/O system --> 운영체제의 하드웨어는 운영체제의 실행 속도를 결정한다.
'Computer Architecture > 컴퓨터구조[01]' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [컴퓨터구조] 2. Instructions: Language of the Computer (2) (0) | 2023.09.18 |
|---|---|
| [컴퓨터구조] 2. Instructions: Language of the Computer (1) (0) | 2023.09.13 |
| [컴퓨터구조] 1. Computer Abstractions and Technology (3) (0) | 2023.09.13 |
| [컴퓨터구조] 1. Computer Abstractions and Technology (2) (0) | 2023.09.10 |
| [컴퓨터구조] 0. Computer Architecture (1) (0) | 2023.09.07 |



