BIOS (Basic Input/Output System)
BIOS는 "Basic Input/Output System"의 약자로, 컴퓨터의 기본 입출력 시스템을 관리하고 초기화하는 소프트웨어입니다. BIOS는 컴퓨터의 부팅 프로세스 중에 실행되며, 컴퓨터 하드웨어와 운영 체제 간의 중요한 인터페이스 역할을 합니다.
- On PCs, the BIOS contains all the code required to control the keyboard, display screen, disk drives, serial communications, and a number of miscellaneous(다양한) functions.
- The BIOS is typically place in a ROM(Read Only Memory) chip.
--> This ensures that the BIOS will always be available and will not be damaged by disk failures.
Technology Trends
- Current Technology: CMOS VLSI (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) (Very Large Scale Integration)
- Trends: Moore's Law
Instruction Sets (MIPS)
- The MIPS instruction set
- Software concerns: procedures, staks, ...
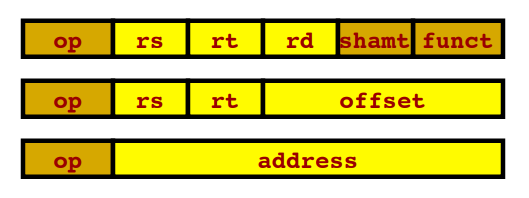
Logic and Arithmetic
- Binary numbers and arithmetic
- Adder & ALUs; multiplication & division
- Floating Point
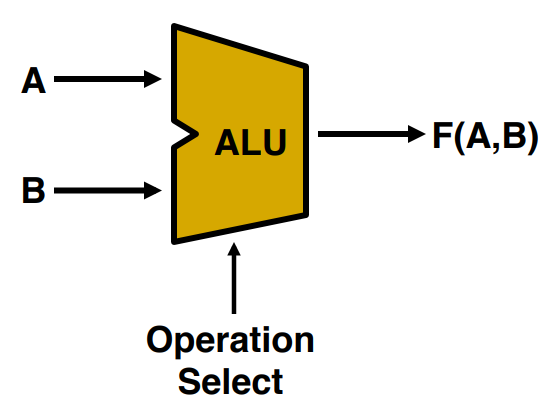
Performance
- Response time(응답시간), Throughput(처리량)
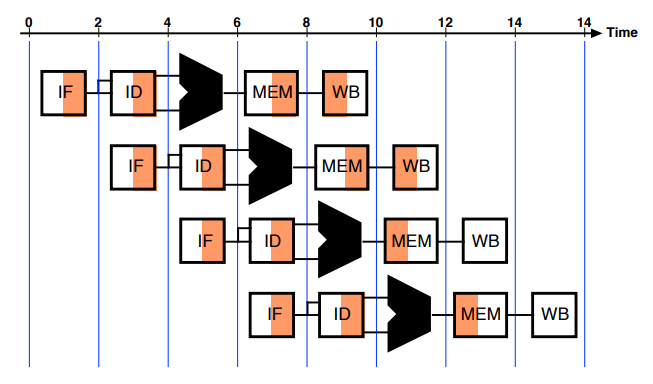
Processor Implementation
- Basic implementation
- Single-Cycle: 1 clock
- Multicycle: multiple clock - Pipelined implementation
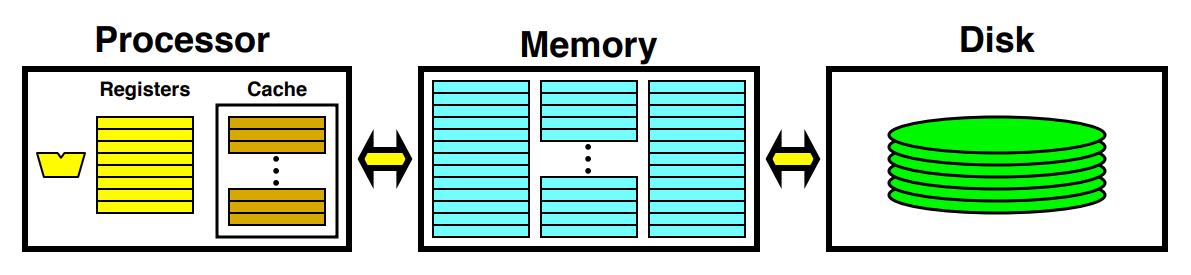
Memory Systems
▶ Memory Hierarchy
- Register
- Cache memory: making access faster.
- Main memory
- Virtual memory: making memory larger using disk.
- Disk
Input/Output
- Impact of I/O Performance
- Buses
- Interfacing
2. Technology Trends
1) Brief History of Computer Technology
SBY 2-1
1. What is BIOS(Basic Input/Output System)?
▶ BIOS(Basic Input/Output System)
: 컴퓨터의 기본 입출력 시스템을 관리하고 초기화하는 소프트웨어 placed in ROM(Read Only Memory) chip.
--> 컴퓨터 하드웨어와 운영체제 간의 인터페이스
- PC에서 BIOS는 keyboard, display screen, disk drive, serial communications, number of miscellaneous(다양한) functions를 control하기 위한 code를 포함한다.
2-1. Can you explain memory hierarchy with some illustrative figures?
▶ Memory hierarchy
: 데이터와 명령을 저장하고 액세스하는 데에 사용되는 메모리 계층 유형
- Register
- Cache memory --> L1, L2, L3
: 데이터 및 명령어를 main memory로부터 빠르게 로드하여 CPU에게 제공하여, 실행 속도를 향상시킨다. - Main memory = RAM(Random Access Memory)
: 프로그램 실행 중에 데이터와 명령어를 저장하는 주 메모리 - Virtual memory
: Making memory larger using disk. - Secondary Storage = Disk
: 비휘발성 메모
2-2. What are cache memory and virtual memory for?
- OS --> RAM(main memory)
- Swap: main memory --> secondary storage(disk)
- Page fault: 만약 프로그램이 RAM(main memory)에서 필요한 정보를 찾지 못하면, OS는 virtual memory에서 찾아와 main memory에 로드한다.
▷ RAM(main memory) <-- virtual memory --> secondary storage(disk)
- RAM, virtual memory: 프로세스의 일부만 main memory에 로드하고, 나머지는 virtual memory에서 보관한다. (어쨌든 실행중인 프로세스의 코드)
- secondary storage(disk): 프로그램 코드의 나머지 부분
'Computer Architecture > 컴퓨터구조[01]' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [컴퓨터구조] 2. Instructions: Language of the Computer (2) (0) | 2023.09.18 |
|---|---|
| [컴퓨터구조] 2. Instructions: Language of the Computer (1) (0) | 2023.09.13 |
| [컴퓨터구조] 1. Computer Abstractions and Technology (3) (0) | 2023.09.13 |
| [컴퓨터구조] 1. Computer Abstractions and Technology (1) (0) | 2023.09.07 |
| [컴퓨터구조] 0. Computer Architecture (1) (0) | 2023.09.07 |



