Performance
CPU Clocking
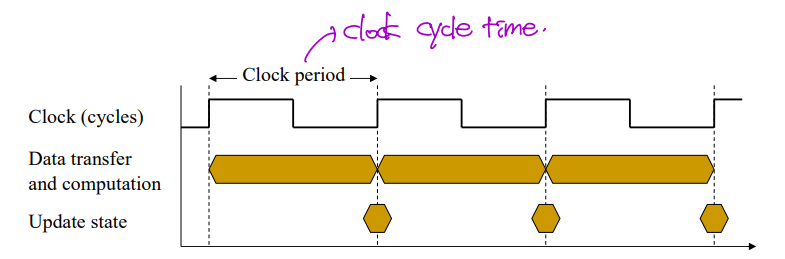
- Clock period: clock cycle 시간
- Clock frequency (rate): clock cycle이 1 초에 몇 번 일어나는가?
CPU Time
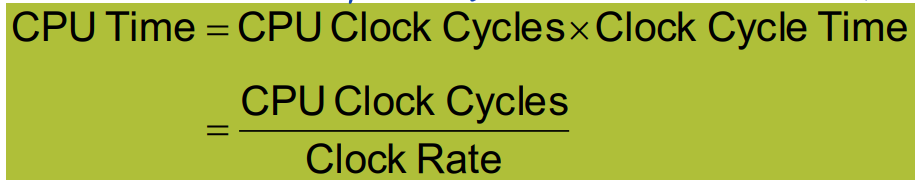
= (clock cycle이 몇 번이나 일어나는가?) * (한 번의 clock cycle에는 몇 초가 걸리는가?)
= (clock cycle이 몇 번이나 일어나는가?) / (clock cycle 속도)
- Clock cycle 횟수를 줄인다. (CPU Clock Cycles ↓)
- Clock 속도를 높인다. (Clock Rate ↑)
Instruction Count & CPI(Clock Per Instruction)
▶ Instruction Count: 몇 개의 instruction이 필요한가?
▶ CPI (Clock Per Instruction): 하나의 instruction 당 몇 번의 clock cycle이 필요한가?
- Clock cycles = Instruction Count * CPI
- CPU Time = Instruction Count * CPI * Clock Cycle Time
(몇 개의 instruction? * 그 하나의 instruction에는 몇 번의 clock cycle이 필요해? * 그 하나의 clock cycle에는 몇 초가 걸려?)
CPI Example
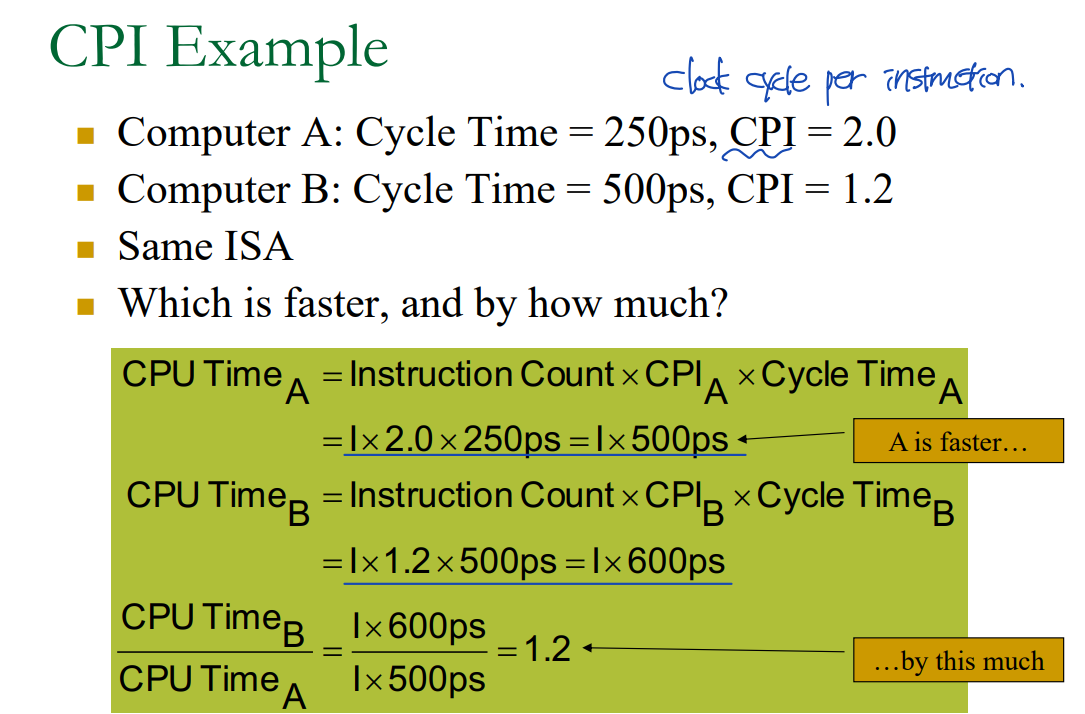
: CPU Time = Instruction Count * CPI * Clock Cycle Time
- CPU Time이 짧으면, better performance!
CPI in more detail
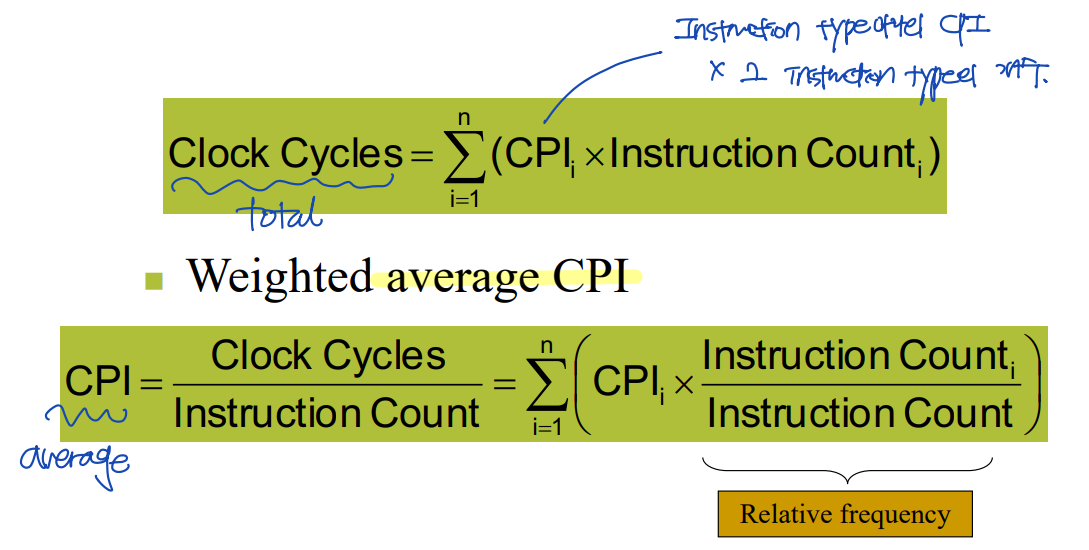
: CPI (Clock Per Instruction)은 instruction마다 다르다.
--> CPU Time을 계산하는데 쓰이는 CPI는 여러 CPI 들의 평균이다.
CPI Example
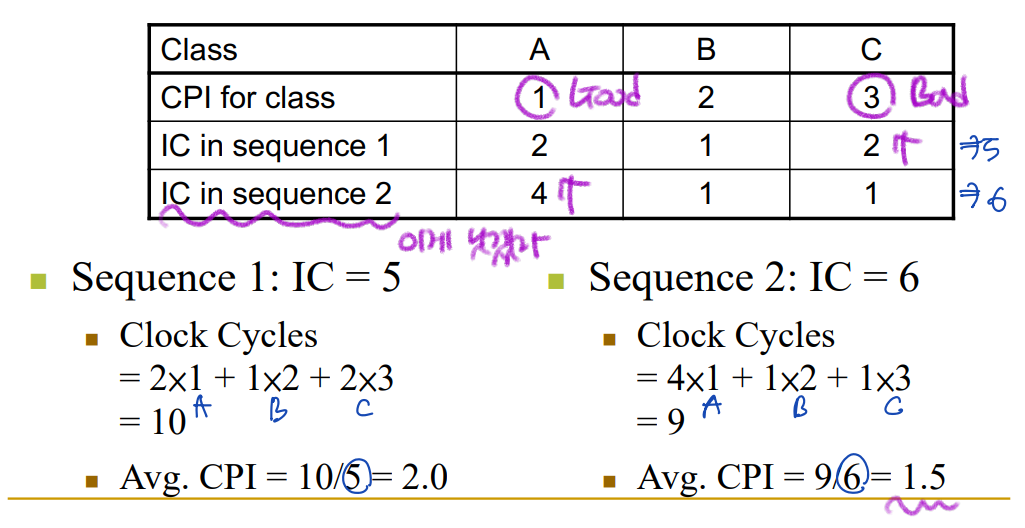
Class A의 CPI(Clock Per Instruction)이 가장 적고, Class C의 CPI가 가장 많다.
그런데 sequence2은 Class A의 비율이 높고, sequence1는 Class C의 비율이 높다.
--> sequence2의 평균 CPI가 더 낮을 것으로 예측할 수 있다.
Performance Summary
▶ CPU Time = Instruction Count * CPI * Clock Cycle Time
▷ Performance depends on:
- Algorithm
- Programming language
- Compiler
- ISA (Instruction Set Architecture)
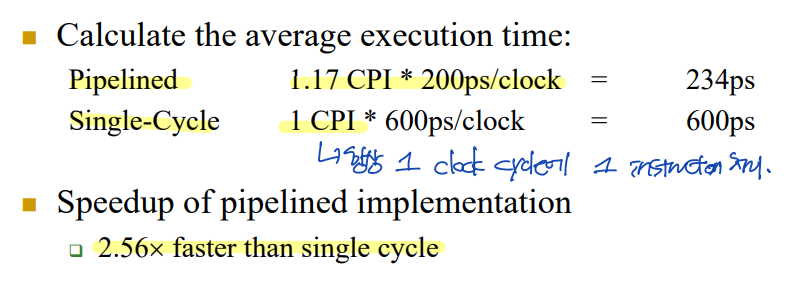
Example: Performance of the Pipelined Implementation
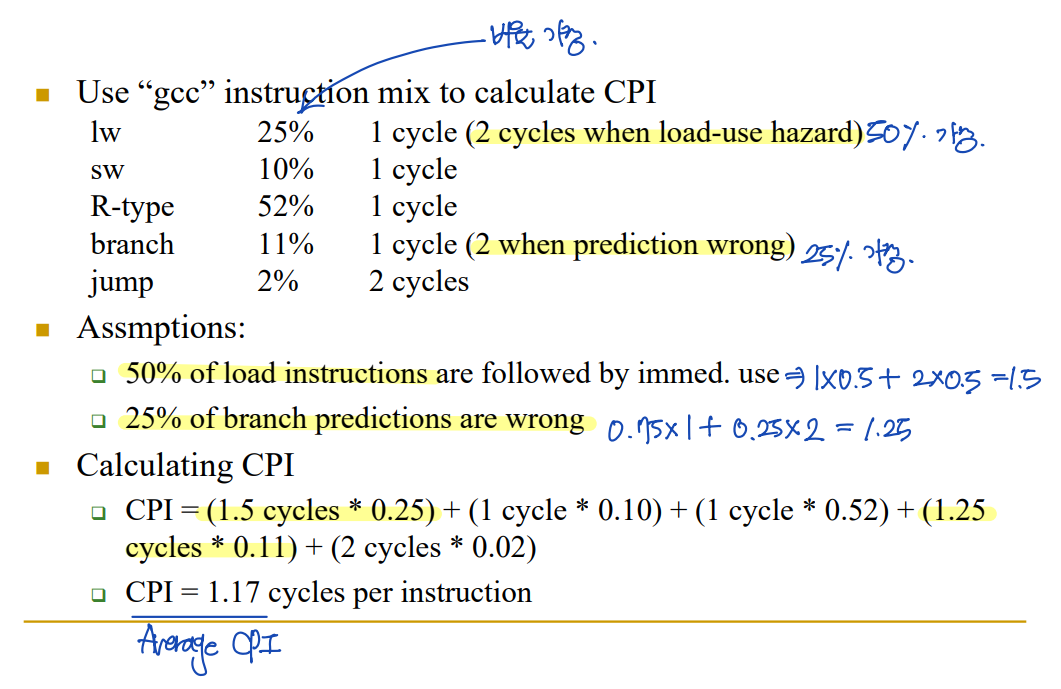
- 각각의 instruction이 발생하는 비율과, Clock Cycle Time을 가정한다.
- - lw: 뒤의 연산에 따라, 1 STALL이 필수적일 수 있다.
- branch: Prediction이 틀리면, 1 STALL이 추가된다. - CPI (Clock Per Instruction) = Clock Cycle Time * Instruction의 발생 확률
--> Pipelined > Single-Cycle
출처: 이화여자대학교 이형준교수님 컴퓨터구조
'Computer Architecture > 컴퓨터구조[01]' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [컴퓨터구조] 1115 (0) | 2023.11.15 |
|---|---|
| [컴퓨터구조] 1113 (2) Ch5. Cache & Memory Systems (0) | 2023.11.13 |
| [컴퓨터구조] 1108 (0) | 2023.11.09 |
| [컴퓨터구조] 1106 (0) | 2023.11.09 |
| [컴퓨터구조] 1101 (0) | 2023.11.05 |



