Pipeline Hazards
- Structural hazard: Attempt to use the same resource twice.
예) 하나의 Memory에 IF와 MEM stage가 겹치면, 문제가 생긴다. - Control hazard: Attempt to make decision before condition is evaluated.
예) branch -- ALU에서 subtraction이 완료되어야 branch 여부를 결정할 수 있다. - Data hazard: Attempt to use data before it is ready.
예) 하나의 Register file에 ID와 WB을 동시에 하면, 문제가 생긴다. (destination이 source가 될 때)
1. Structural Hazard
: Attempt to use the same resource twice at the same time.
예) Single Memory for instructions(IF; Instruction Fetch) and data(MEM; Memory access).
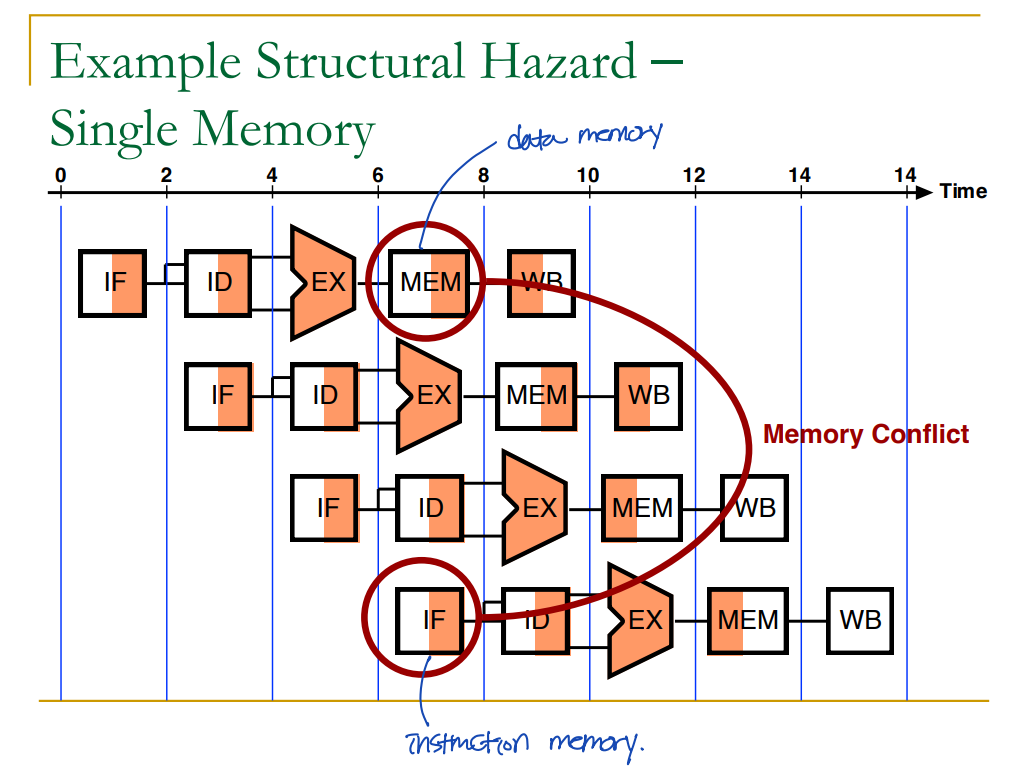
Solution 1) Stall
: 1 clock cycle만큼 기다린다.
Solution 2) "Harvard Architecture"
: IF와 MEM을 위한 메모리를 따로 둔다.
- Instruction memory
- Data memory
- Real pipelined processors have separate caches.
즉, 메모리 level과 캐시 메모리 level 모두에서 separate memory를 둔다.
2. Control Hazard
: Attempt to make a decision before condition is evaluated.
예) branch - ALU stage에서 subtraction이 완료되어야, branch 여부를 판단할 수 있다.
Solution 1) Stall
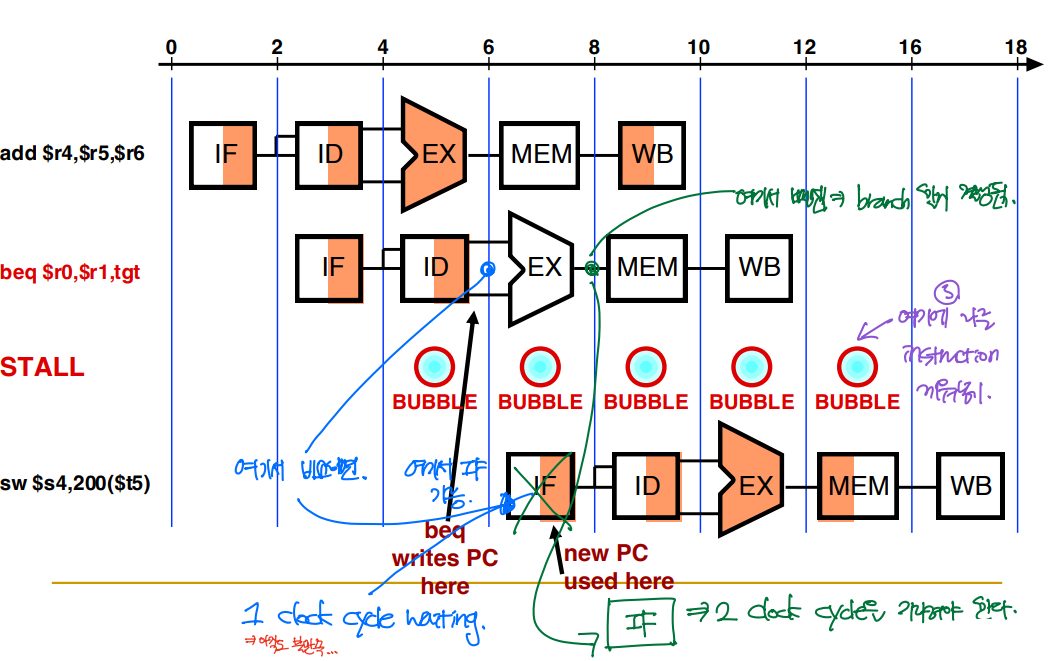
원래는 ALU stage에서 subtraction을 통해 두 레지스터 값을 비교하고, Zero control이 1인지 0인지에 대한 판단이 끝나야 새로운 PC 값을 설정하는 IF 단계를 수행할 수 있다. 그렇다면, 2 clock cycle waiting이 필요해진다.
만약 레지스터 값들의 비교를 ALU stage 이전에 수행한다 하더라도, 1 clock cycle waiting은 불가피하다. --> STALL
Solution 2) Predict

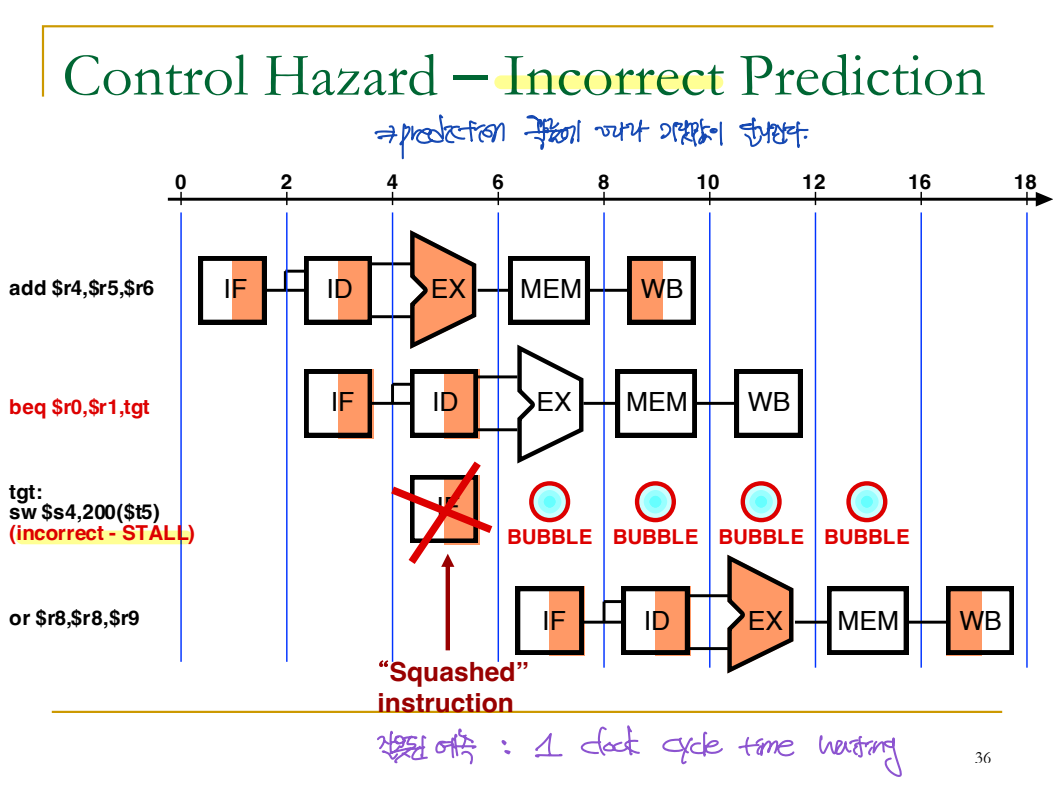
--> 맞게 예측할 확률(0.5)*0 + 틀리게 예측할 확률(0.5)*1 = 0.5
Solution 3) Delayed Branch
: STALL할 자리에 상관없는 instruction을 끼워 넣는다.

3. Data Hazard
: Attempt to use data before it is ready.

Solution 1) Stall

$s0로 WB된 다음에야 ($s0 - $t3)을 할 수 있다.
따라서, add의 WB stage 다음에, sub의 ALU stage가 나올 수 있다. --> 2 clock cycle time waiting.
Cf) lw: 2 clock cycle time waiting (똑같음)
Solution 2) Forwarding
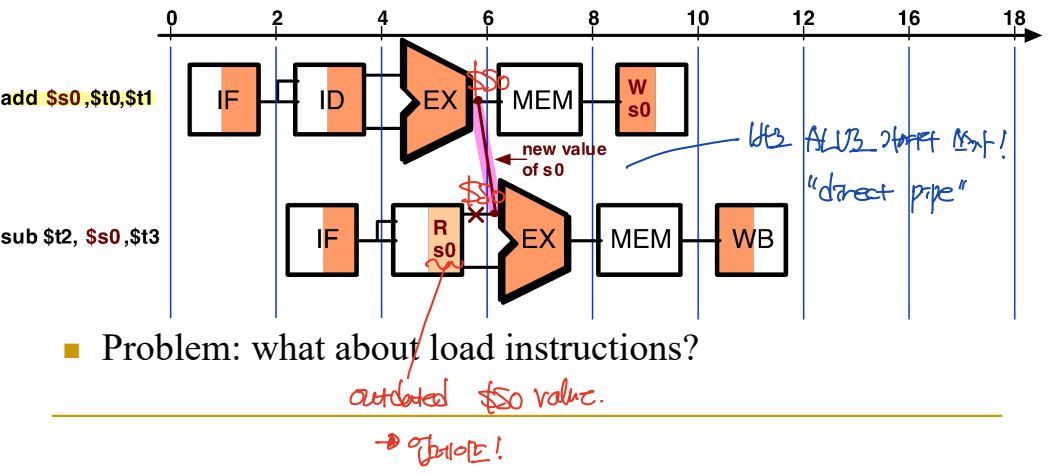
- Direct pipe: ($t0 + $t1) 값을 $s0에 WB하기 전에, ALU 단계를 마친 후 바로 그 값을 sub의 ALU stage로 가져온다.
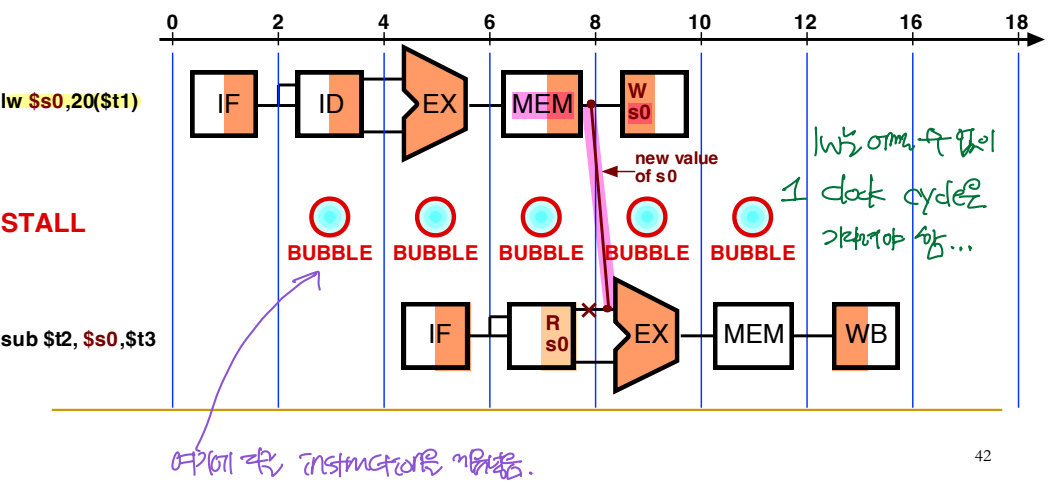
lw에서는 ALU에서 연산한 후, 메모리에 접근하여 memory read 후, 그 값을 $s0에 저장해야 한다. 따라서 MEM 단계 이후에 sub의 ALU 연산을 할 수 있다. --> 1 clock cycle waiting은 불가피하다.
Solution 3) Reordering instructions
: instruction들의 순서를 바꿔서, waiting을 없앤다.

Summary - Pipelining Overview
- 파이프라이닝을 이용하면, 하나의 instruction에 대한 execution time은 변하지 않지만, total execution time이 줄어들기 때문에, throughput이 증가한다.
- Hazard limit performance
- Structural hazards
- Control hazards
- Data hazards
Pipelining in MIPS
: MIPS architecture was designed to be pipelined.
- Simple instruction format.
- Memory operations only in lw, sw instructions.
- Memory operands aligned in memory.
- Single value for write back.
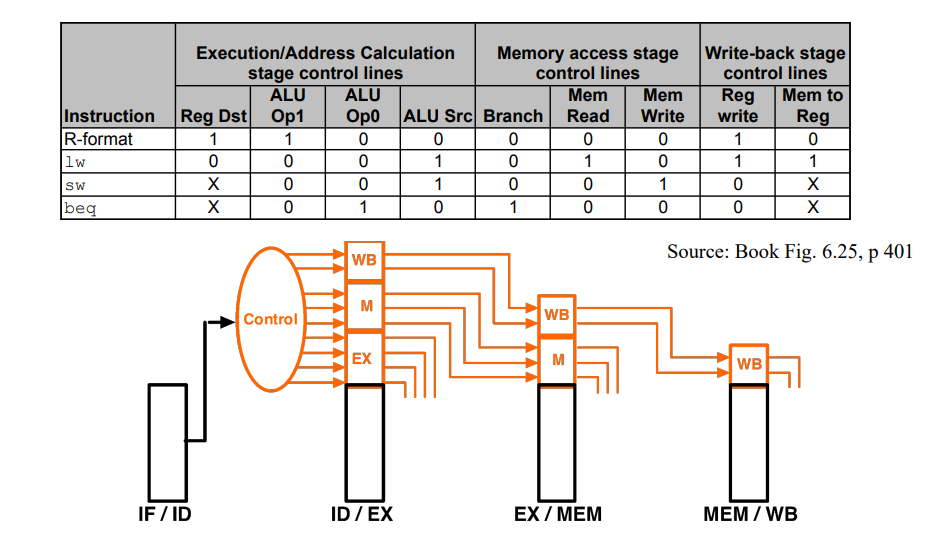
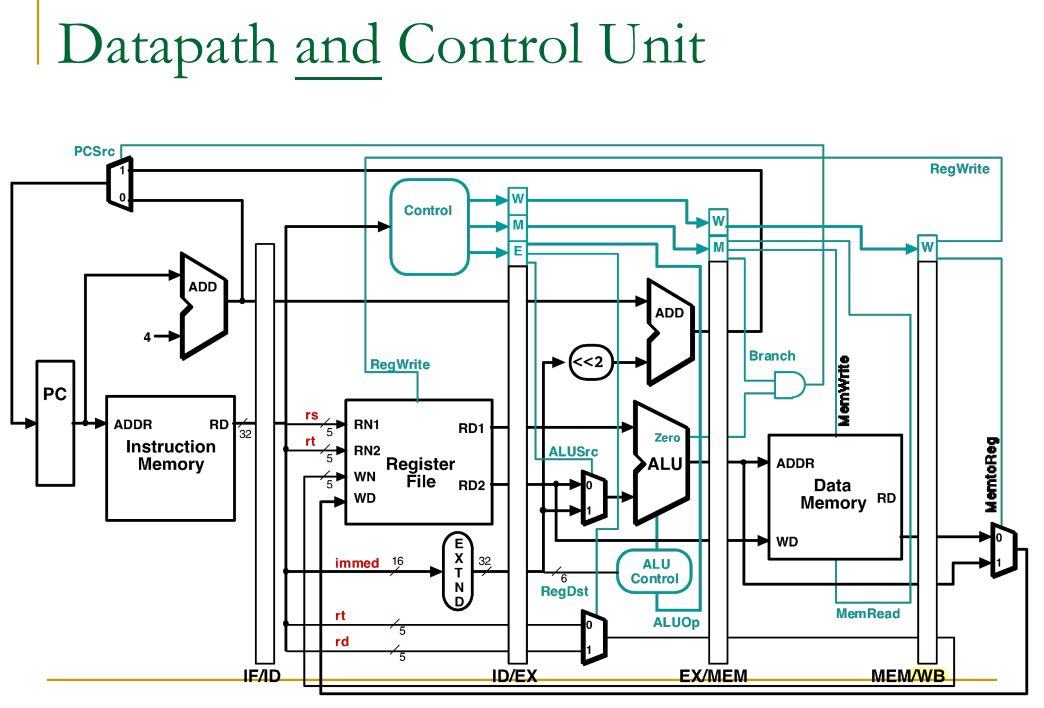
Pipelined Datapath with Control Signals

--> 이제 여기에 control을 추가할거야.
Control for Pipelined Datapath
Tracking Control Signals
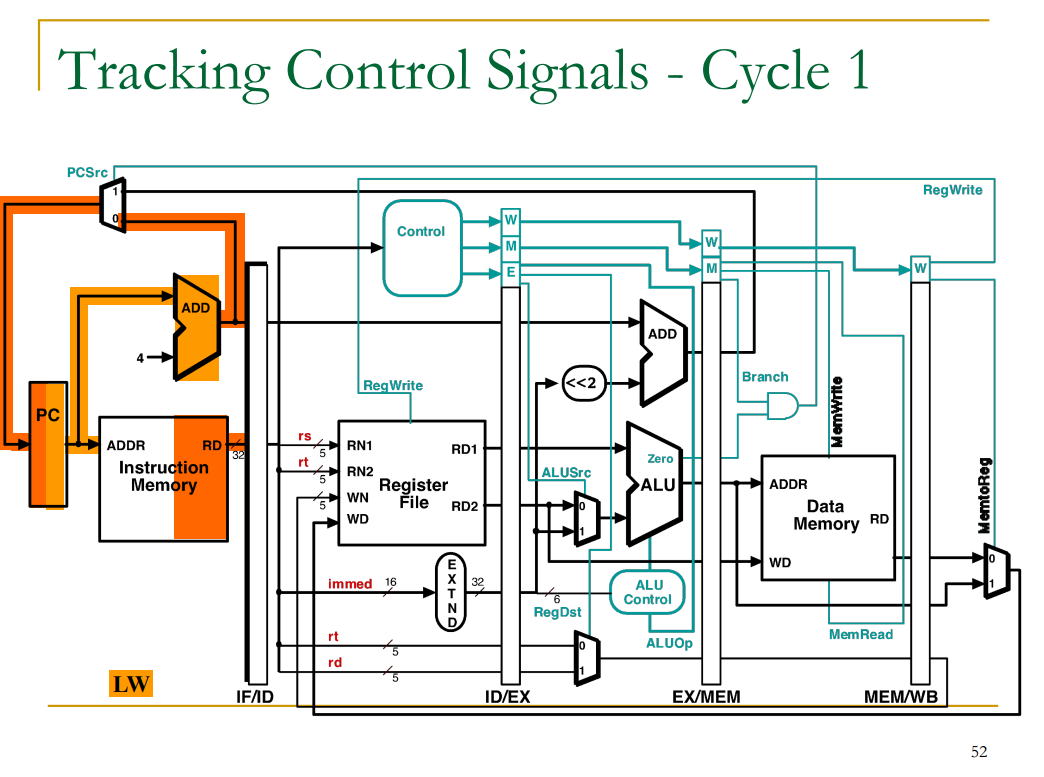
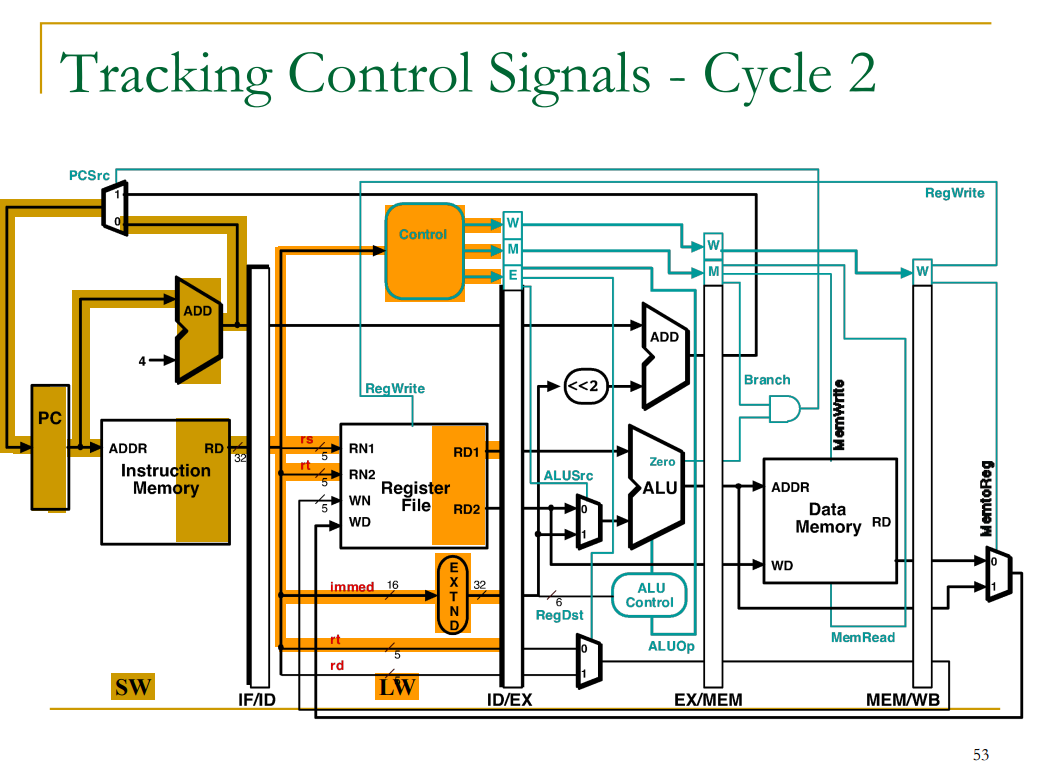

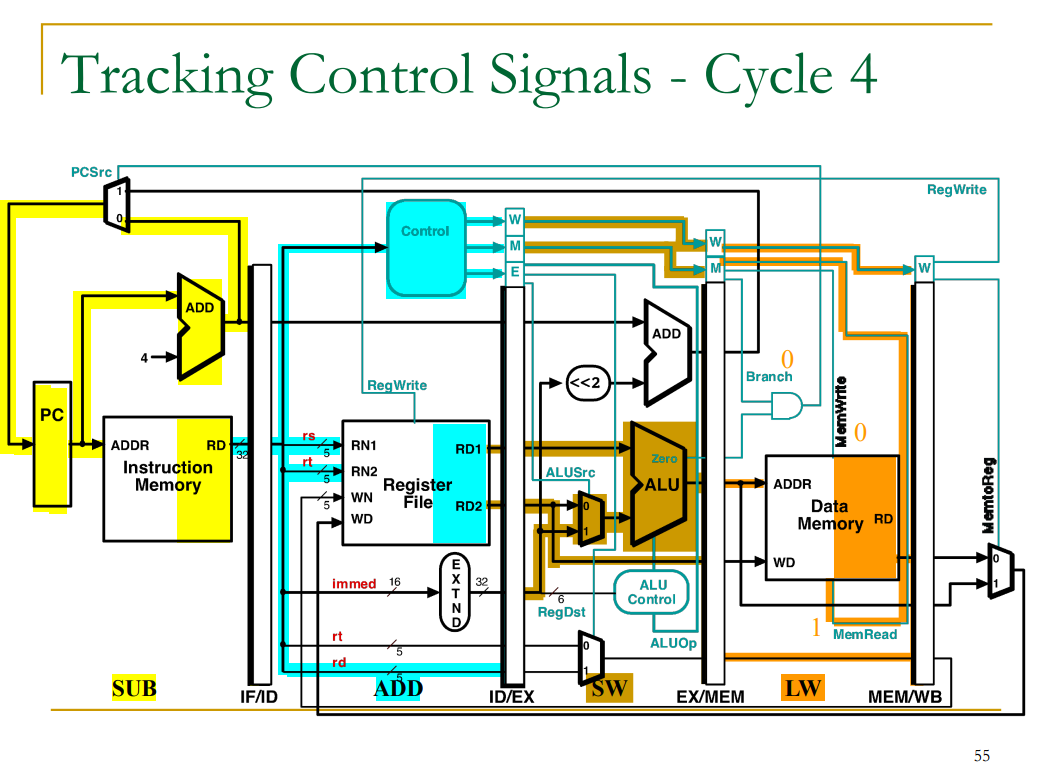
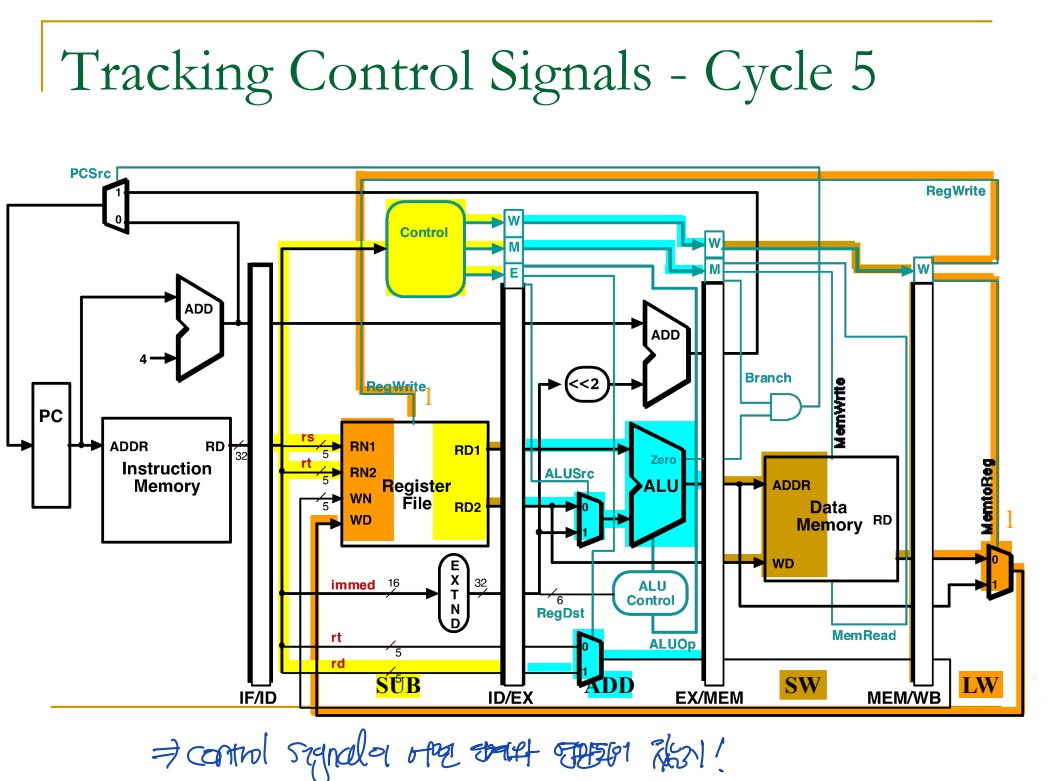
출처: 이화여자대학교 이형준교수님 컴퓨터구조
'Computer Architecture > 컴퓨터구조[01]' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [컴퓨터구조] 1108 (0) | 2023.11.09 |
|---|---|
| [컴퓨터구조] 1106 (0) | 2023.11.09 |
| [컴퓨터구조] 1030 (1) | 2023.11.02 |
| [컴퓨터구조] 4. The Processor (1) (0) | 2023.10.22 |
| [컴퓨터구조] 3. Arithmetic for Computers (4) (0) | 2023.10.22 |



